I still remember learning about osmosis at school many years ago. I don't know why that particular memory has stayed with me so strongly, maybe because it was hard to understand. Whatever the reason, osmosis is a term I've never forgotten the meaning of.
Definition of Osmosis
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
or
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
The important thing to remember is that osmosis is the movement of WATER MOLECULES( or other solvent ), not the particles dissolved in the water. For example if you split a beaker of water into two halves with a semi permeable membrane and added salt to one side, water would move from the side of the beaker with no salt into the salty side.
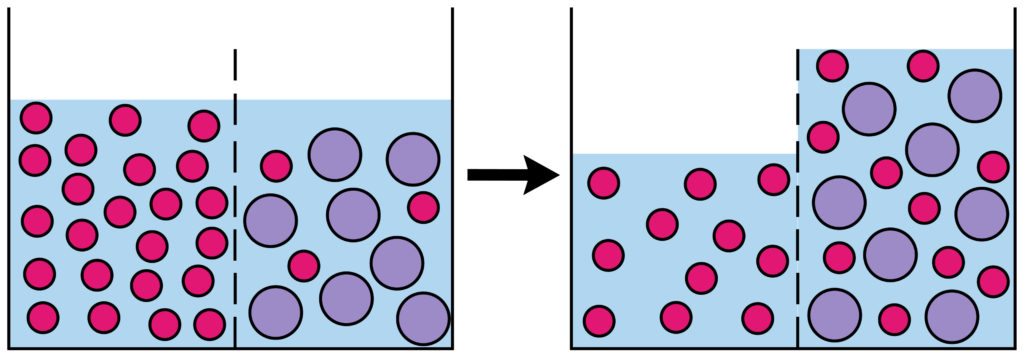
What is a partially permeable membrane?
A partially permeable membrane has very small holes in it. Tiny water molecules can fit through, but not bigger molecules like sugars.
Osmosis Example
Try soaking a raisin in water. What happens? It should swell up a little. This is because the water moves from where it is in high concentration ( the water ) into the raisins which have a low water concentration. Water keeps moving by osmosis until equilibrium is reached, this is when the concentration of both solutions is the same.
Another fun way to illustrate osmosis is with eggs as they have a handy semi-permeable membrane.
Easy Osmosis Experiment
You'll need
Two eggs
Water
Two glasses or jars
Vinegar
Sugar
A pin
Remove the shell from two eggs
Place two eggs in a container of vinegar for about 24 hours. The eggs should be completely submerged.
After about 24 hours, remove the eggs and gently rub the shell under cold running water. You should be able to remove most of the shell.
If it won't all rub off, put the eggs in fresh vinegar for another few hours.
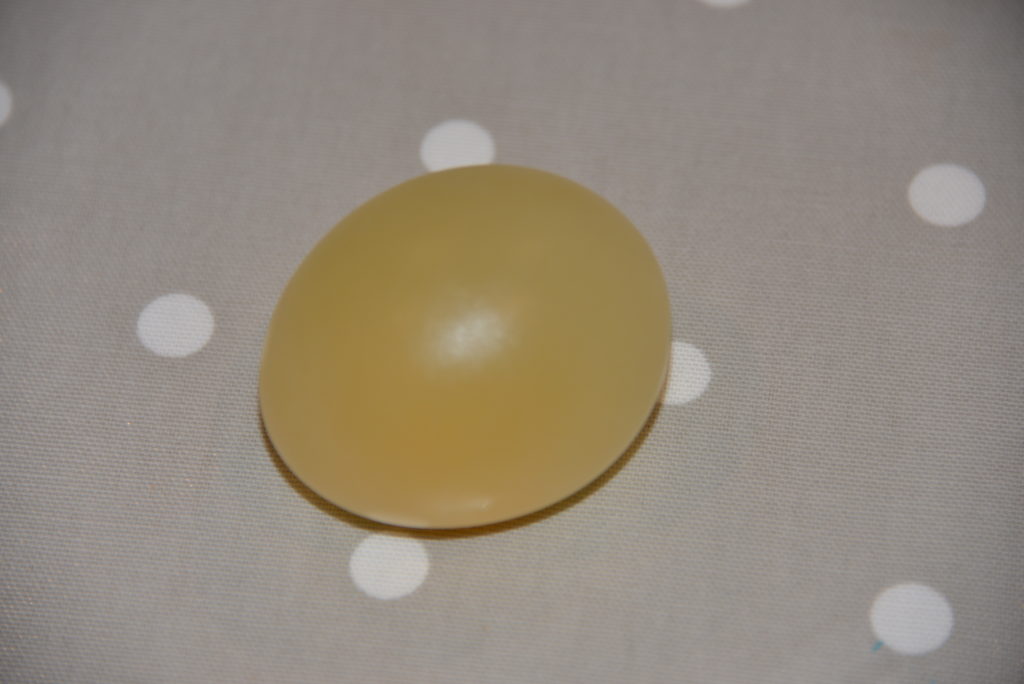

Shrink an egg
To shrink the egg you need to put in in a concentrated solution so water molecules will move from the egg into the solution..
Stir about three tablespoons of sugar into a glass of water and stir until all the sugar has dissolved.
Place one egg in this solution.
Grow an egg
Place the second egg in a glass of plain water.
Leave the eggs for about 24 hours. Can you predict what will happen?
Note how the egg in the water sinks to the bottom of the glass while the one in the sugar solution floats. This is because the sugar solution is more dense than the water.
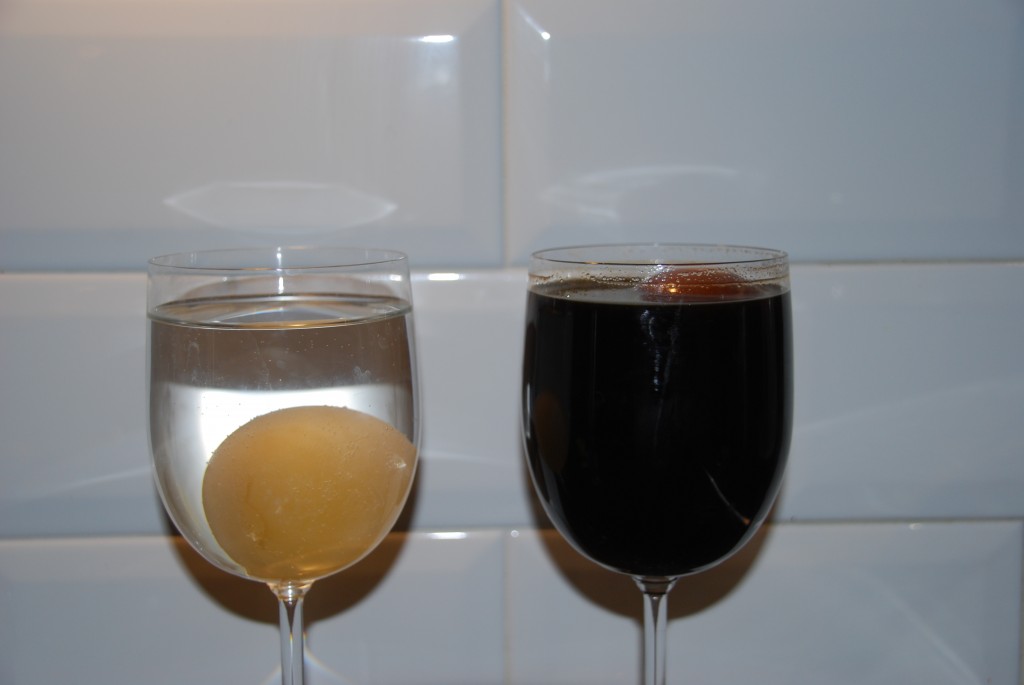

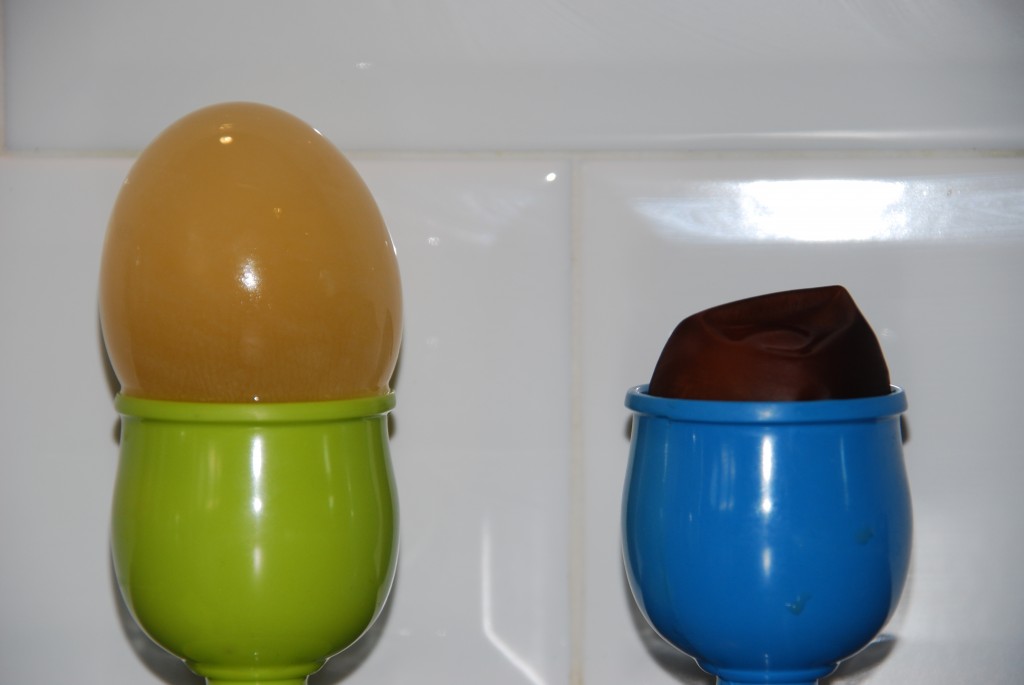
Our egg in the water expanded while the egg in the sugar solution shrank. I used dark sugar, which is why the solution looks brown/red, but any sugar will work.

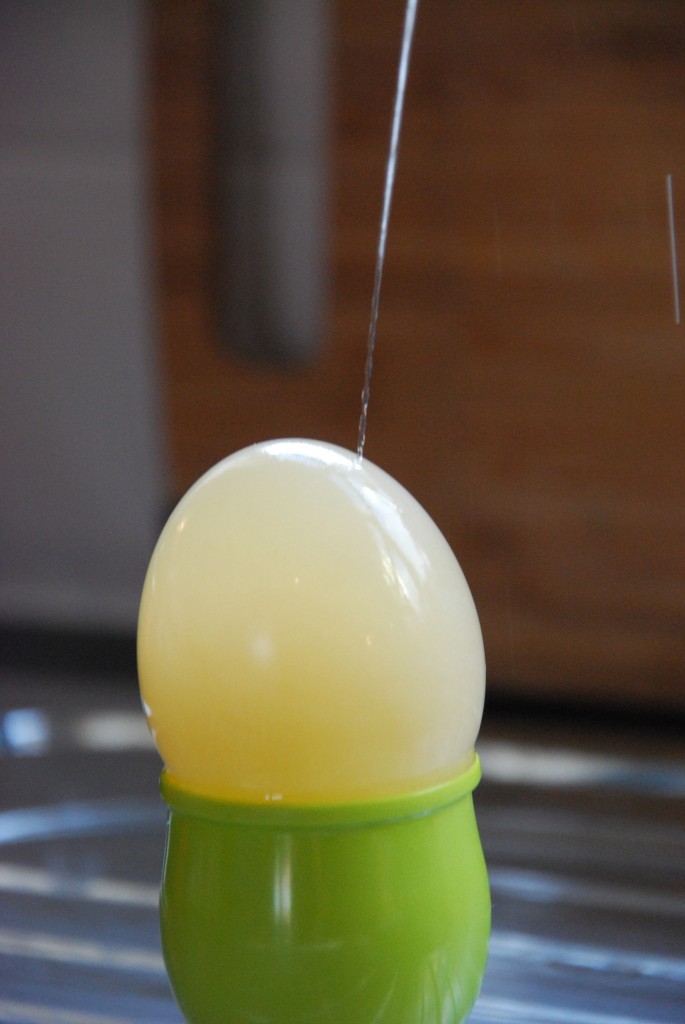
Prick the egg from the water with a fine needle and watch a jet of water shoot out!

How do you think you could rehydrate your shrunken egg?

Why does the egg grow and shrink?
Our concentrated solution was the sugar solution. The dissolved sugar molecules cannot pass through the semi-permeable membrane of the egg, but the smaller water molecules can. Water molecules move from where they are in higher concentration ( inside the egg ) to where they are in lower concentration ( the sugar solution ) until equilibrium is reached. Therefore water molecules move from inside the egg to the sugar solution. This makes the egg shrink as the net movement of water is out of the egg.
To rehydrate the egg, place it in plain water. In this instance the concentration of water molecules is higher in the water than inside the egg so the net movement of water molecules is from the water into the egg!
When we pricked the egg soaked in water, water shot out. This is because the egg had absorbed so much extra water that the pressure inside increased.
Why does egg shell dissolve in vinegar?
The egg shell dissolves in the vinegar as the acetic acid reacts with the calcium carbonate of the shell. Carbon dioxide is given off during this reaction, which is the bubbles of gas you see.
More osmosis experiments
Weigh the eggs at each stage to monitor the loss and gain of water.
Add food colouring to the water and watch the eggs absorb the coloured liquid.
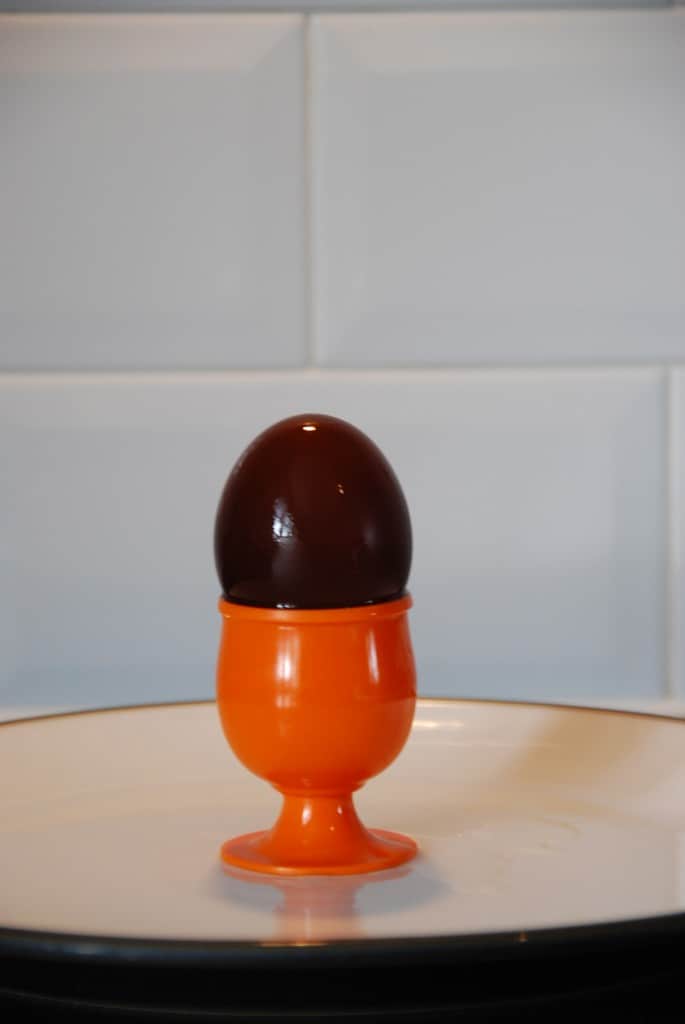
What do you think would happen if you left an egg in a glass of golden syrup?
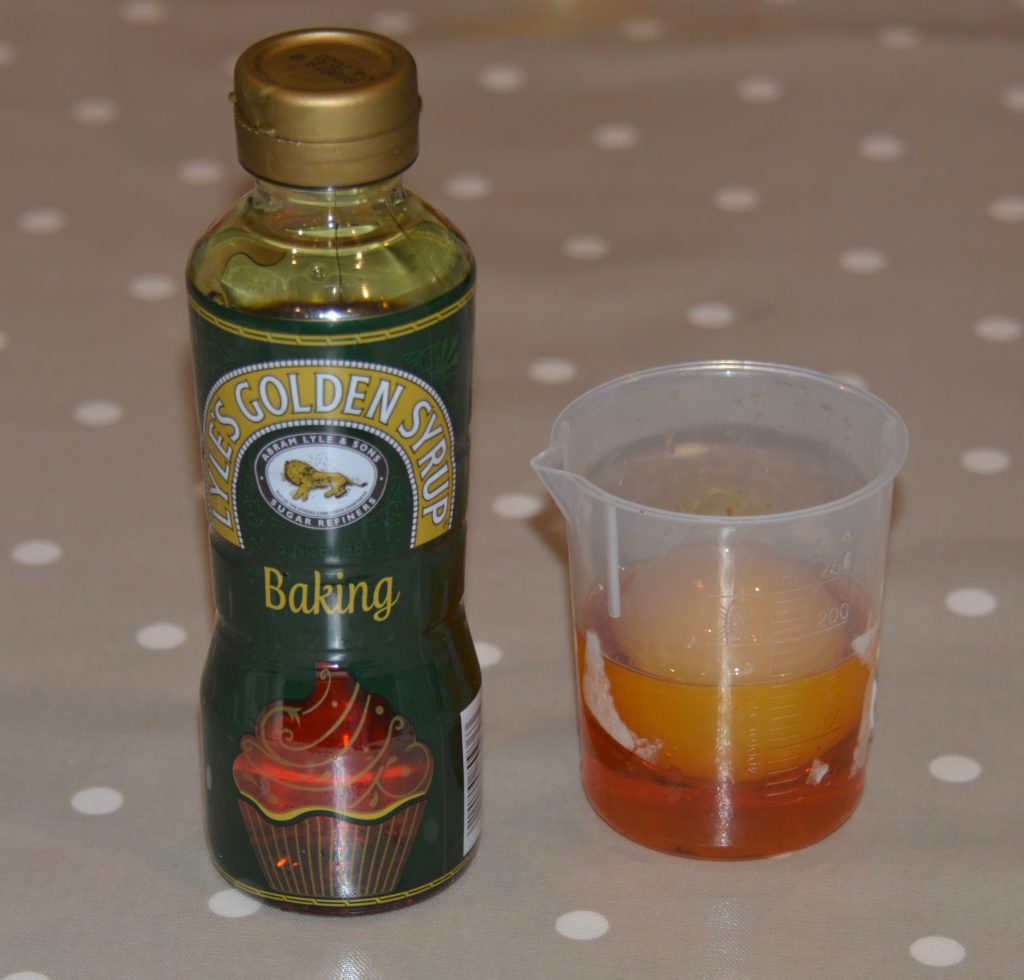

Try measuring the egg at each stage of the investigation.
We used thread to measure the diameter of the egg at its widest point after the shell was first removed, after soaking in vinegar and after soaking in golden syrup.
The longest thread is from when the egg was soaked in water. This is because the concentration of water inside the egg was lower than outside the egg, so water moved into the egg.
The shortest thread is from the egg soaked in golden syrup. Water moved by osmosis out of the egg into the golden syrup because the concentration of water inside the egg was higher than outside.

Don't forget to wash your hands after handling raw eggs
More egg experiments for kids
Learn about tooth decay with eggs. Did you know an egg shell is similar to the outer coating on our teeth?

Find out how to transform egg white into meringue and make a tasty dessert at the same time.
Finally, did you know you can make an egg bounce?


Last Updated on September 19, 2024 by Emma Vanstone



Shirley de Bruyn says
I would like to receive your newsletter, please?