Creating a 3D neurone ( or neuron ) model is a great way to learn about the central nervous system and how messages are transmitted around the body.
3D neurone models are also a fantastic addition to a school science fair project about the nervous system.
What are neurones?
Neurones ( often called nerve cells ) are specialised cells found all over the body. They carry electrical signals.
Neurones are often very long to speed up nerve impulses. Connections between neurones, although fast, slow the impulse down, so one long neurone transmits a message faster than lots of smaller ones.
What is the central nervous system?
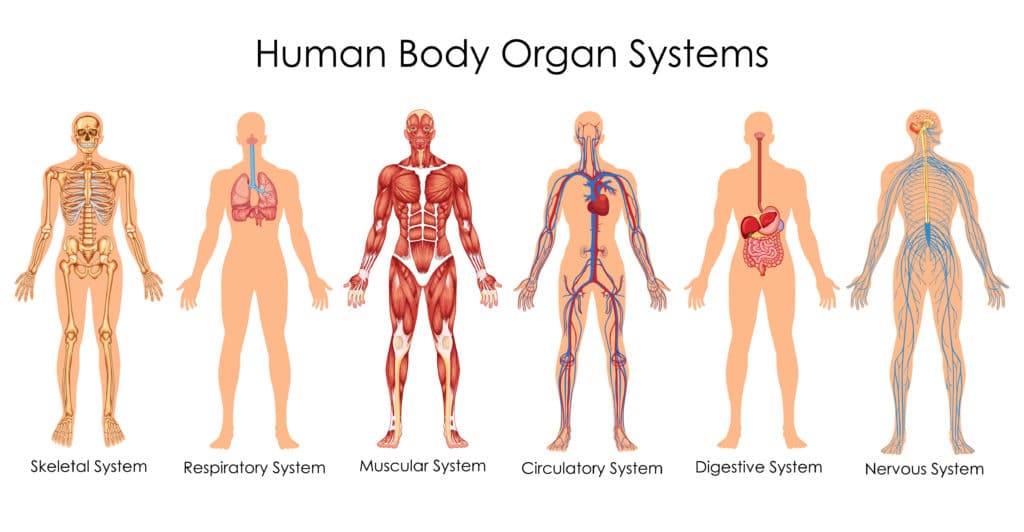
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system is all the nerve cells that carry information to and from the central nervous system.
Neurones are part of the nervous system. Humans have five sense organs ( eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin ). These contain nerves which send messages to the brain about whatever stimuli they detect. The brain then decides on a response that it sends via more nerve cells to the part of the body that needs to respond.
What are receptor cells?
Receptor cells are specialised cells in the sense organs, and effectors are the part of the body that responds to a stimulus, such as muscle cells.
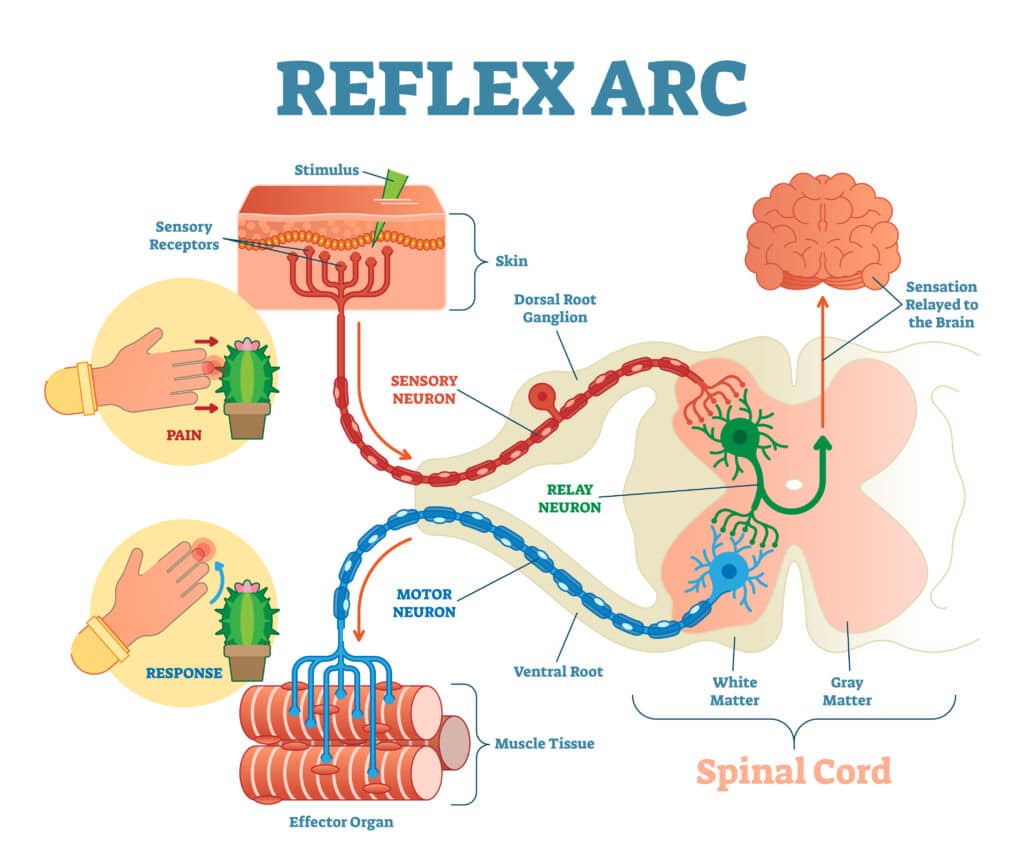
Information flow from receptors to effectors
Stimulus - Receptor - Sensory neurone - CNS - Motor neurone - Effector - Response
As you can see, there are several different types of neurones, including sensory neurones, motor neurones and relay neurones. Each has a slightly different structure.
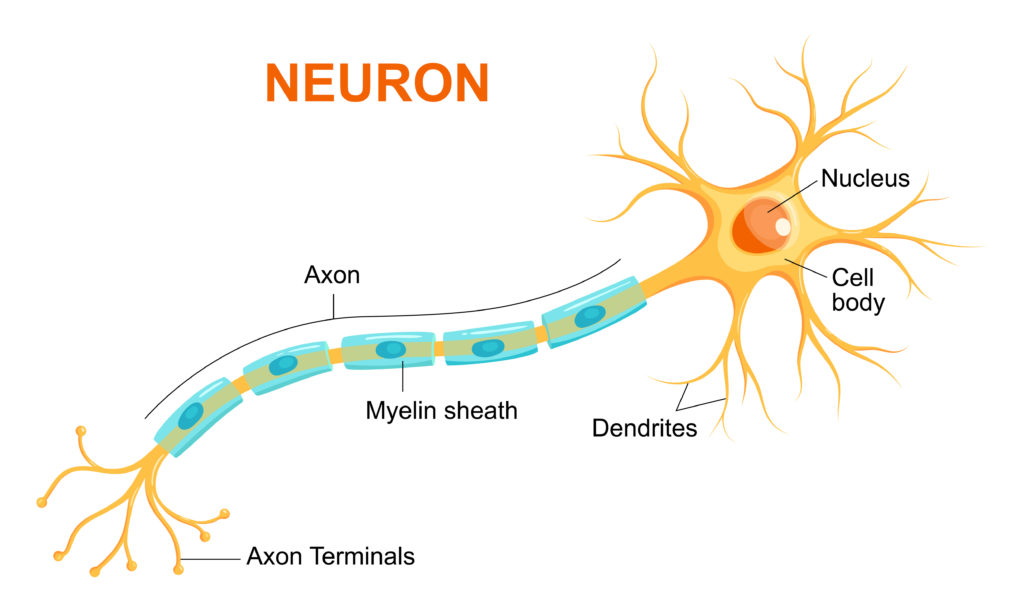
Neuron structure
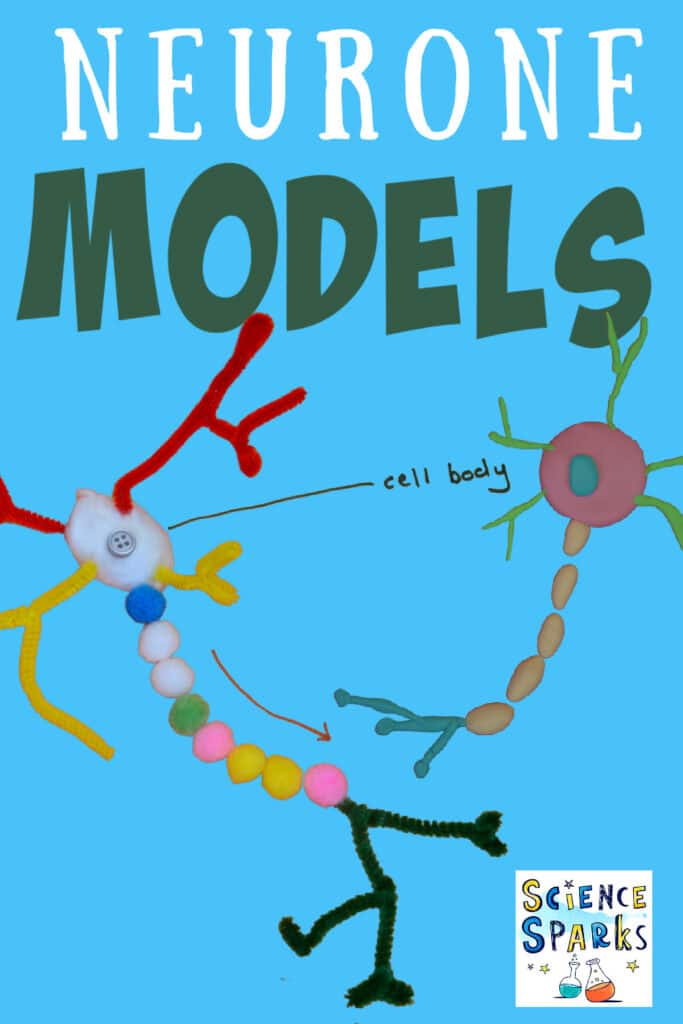
Neurones have a cell body with a nucleus, cytoplasm and other sub-cellular structures.
Unlike other cells, neurones have extensions that connect to other neurones.
Dendrites and dendrons carry impulses towards the cell body. They pick up impulses from other neurones.
Axons carry impulses away from the cell body to other neurones.
Neuron Models
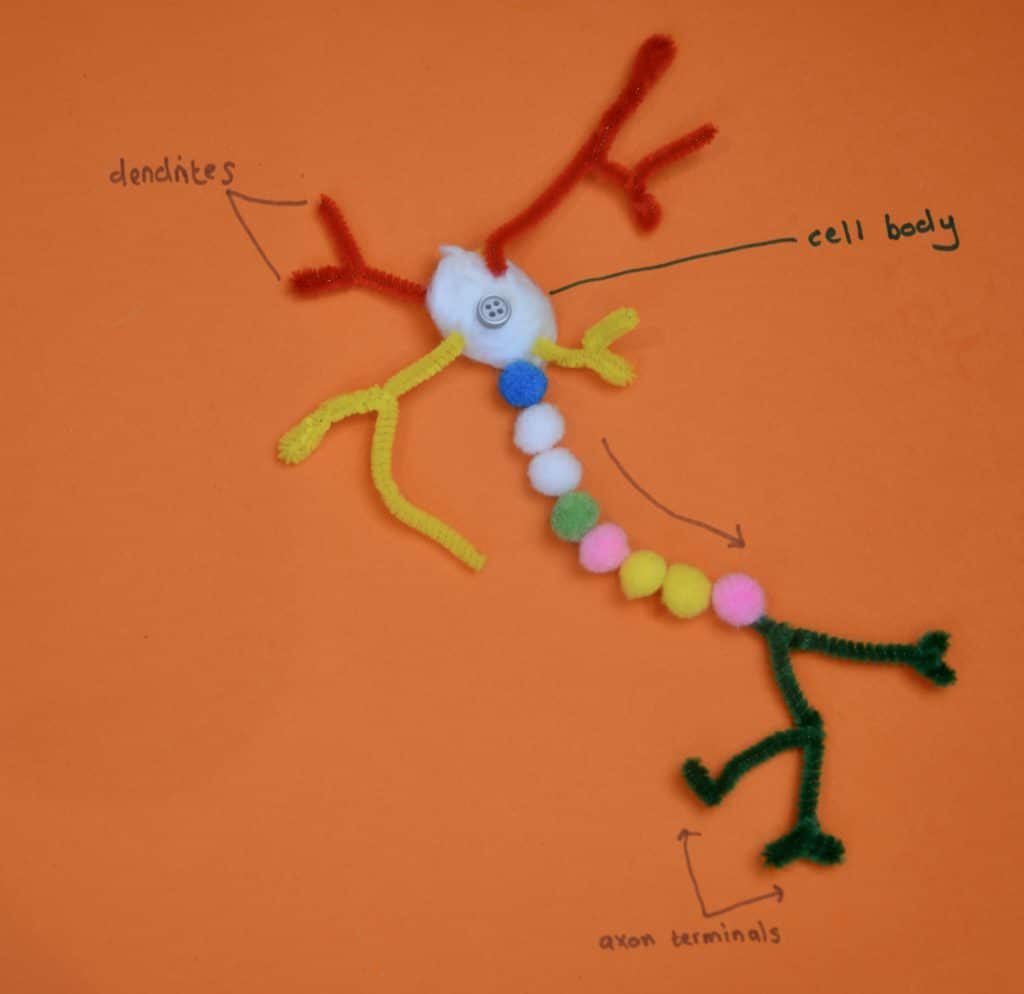
Pipe cleaner neurone model
The neurone model below is made from pipe cleaners, cotton wool and small pom poms.
The pom poms represent the myelin sheath found around some axons. The myelin acts as an insulator to speed up the electrical impulse.
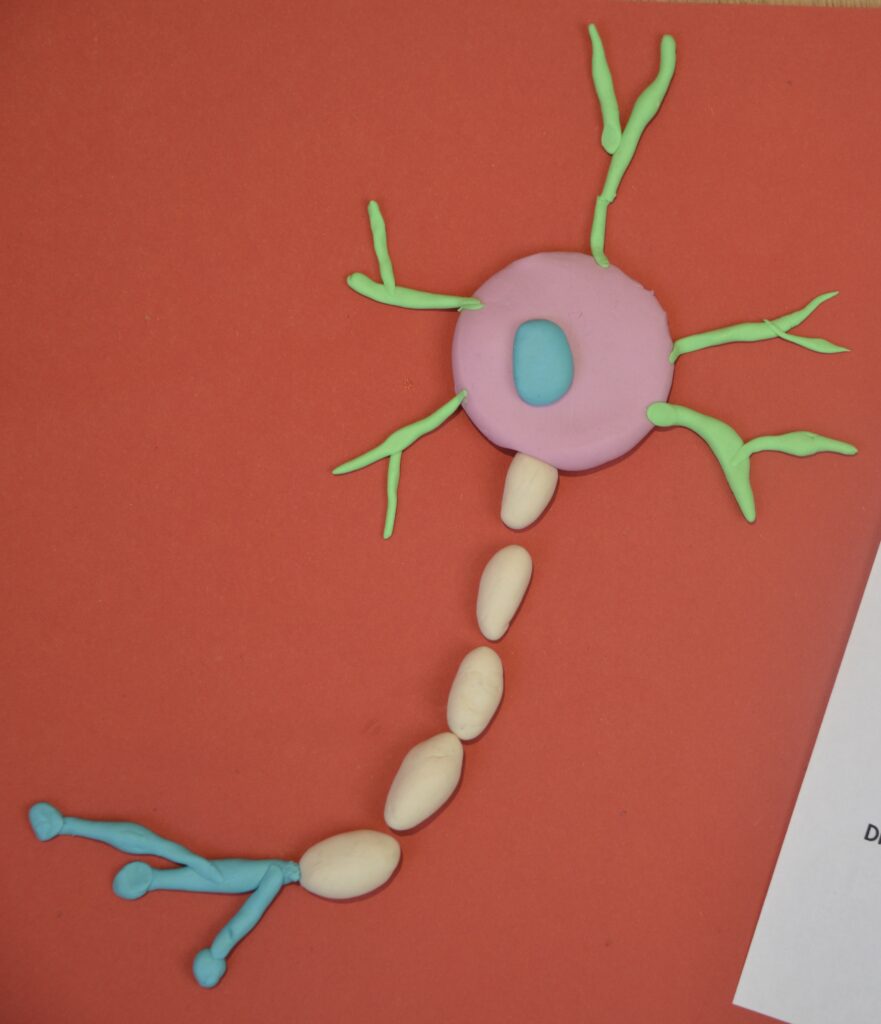
Play dough neurone model
This is a straightforward neurone model made using play dough.
Other ideas for neurone models are to use sweets, modroc or beads!
What is reaction time?
Reaction time is the time it takes you to respond to a stimulus. One easy way to measure reaction time is using a ruler!
What is a reflex arc?
A reflex action is an automatic, very fast response to stimuli. For example, if you touch something very hot or sharp, your reflex action is to move your hand away. A reflex response is faster than a normal response as it requires less thought processing. The impulses travel via the spine or unconscious part of the brain, and the conscious part of the brain is bypassed to save time.
Last Updated on April 11, 2023 by Emma Vanstone




Leave a Reply