Cells are the fundamental units of life where most of the essential chemistry and functions that keep us alive happen. Cells are the building blocks of every organism and make up most of the structures within the body.
Facts about cells
- All living things are made of cells.
- Cells can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
- Every new cell originates from an existing cell, which divides to form new cells.
- Cells are viewed and studied using a microscope.
- Cells work together in groups called tissues.
- Tissues work together to form organs.
- Cells contain organelles. Each organelle has a different job.
- Different cells have different functions. Specialised cells are those which are adapted to their function. Examples of specialised cells are sperm cells, nerve cells, egg cells, and ciliated epithelial cells.
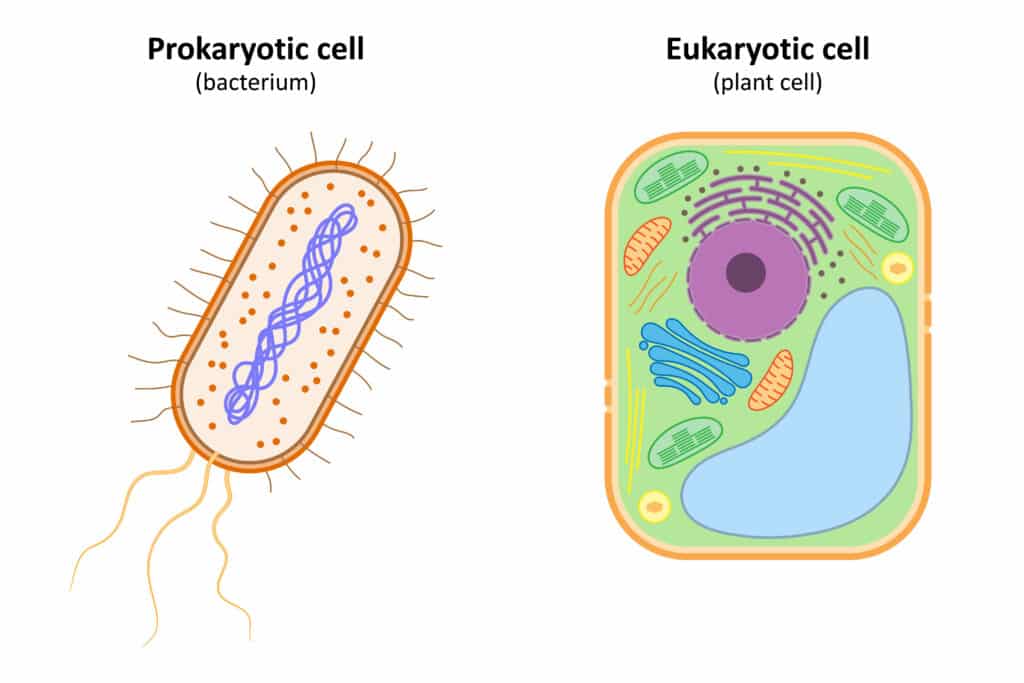
What's the difference between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells and don't have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells and are usually single-celled organisms.
Examples of prokaryotic cells
- Bacteria
- Archaea
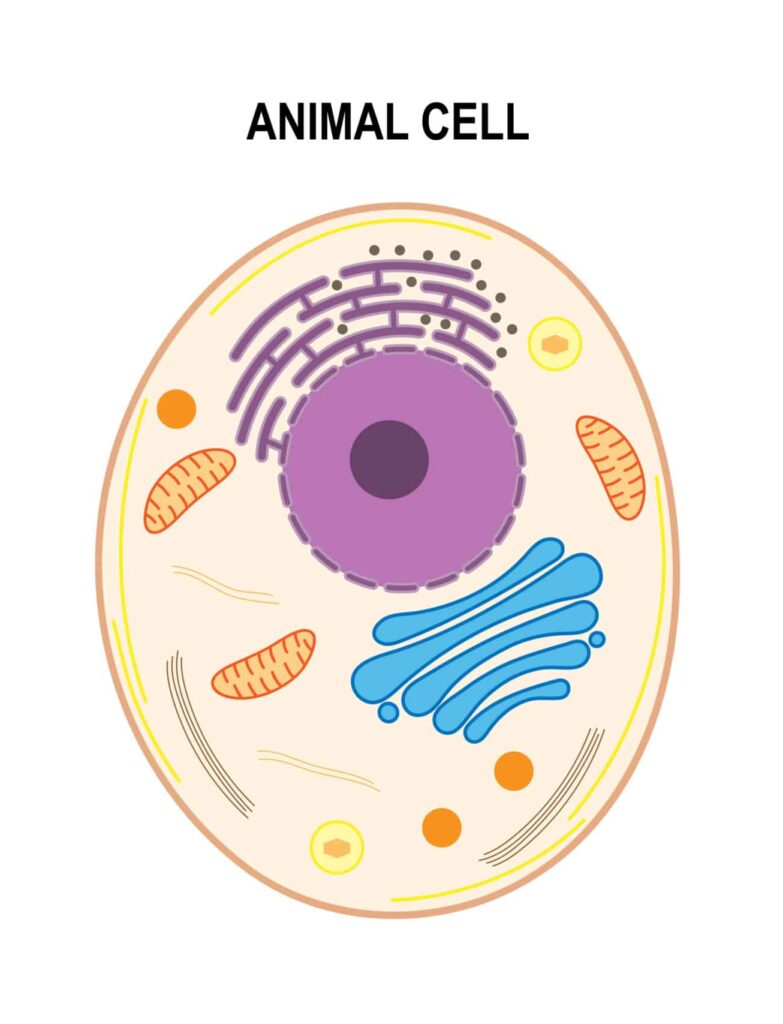
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. They have a defined nucleus and organelles. All animal and plant cells are eukaryotic.
Eukaryotic cells can be single-celled or multicellular organisms.
Examples of eukaryotic cells
- Animal cells
- Plant cells
- Fungi
- Protists
Easy science activities for learning about cells
Now that you know what a cell is, try some hands-on activities to learn more about them.
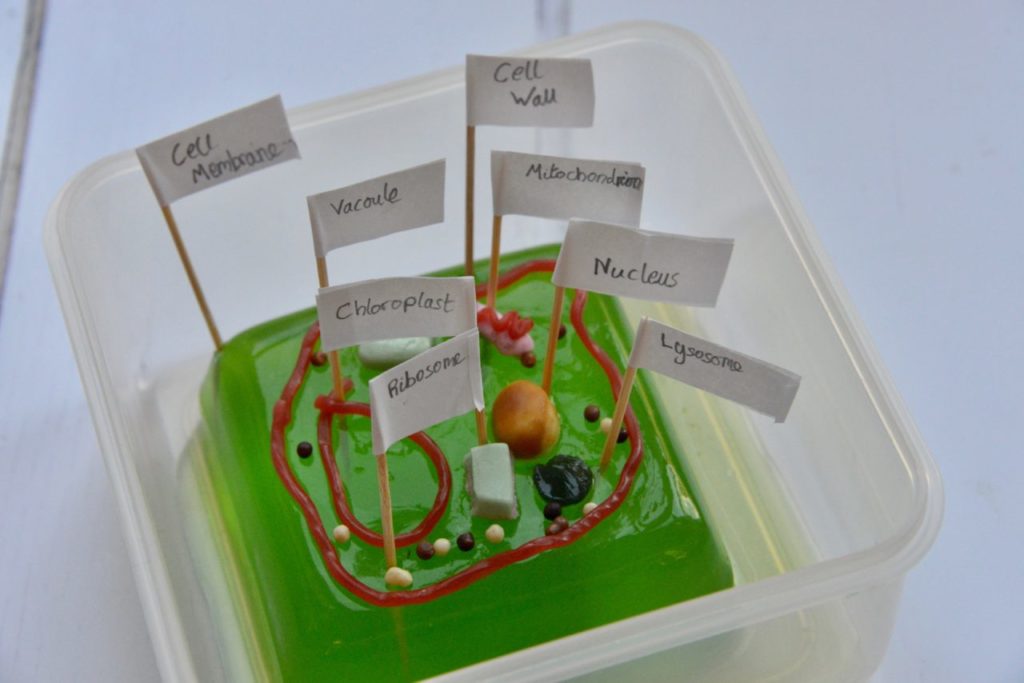
DIY Cell models
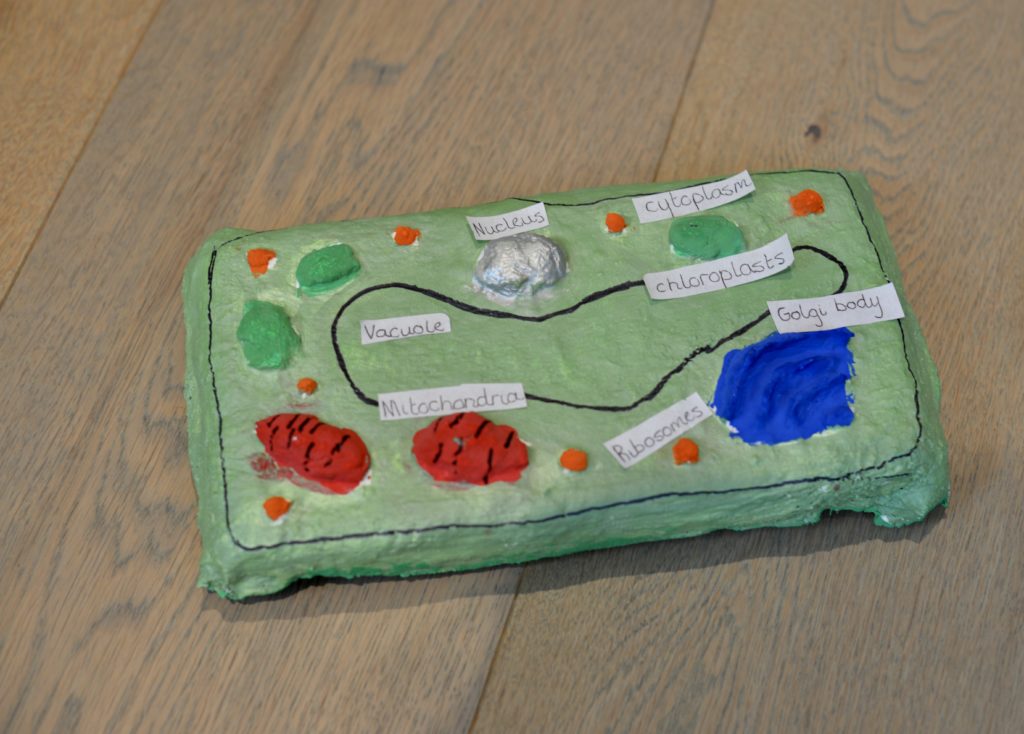
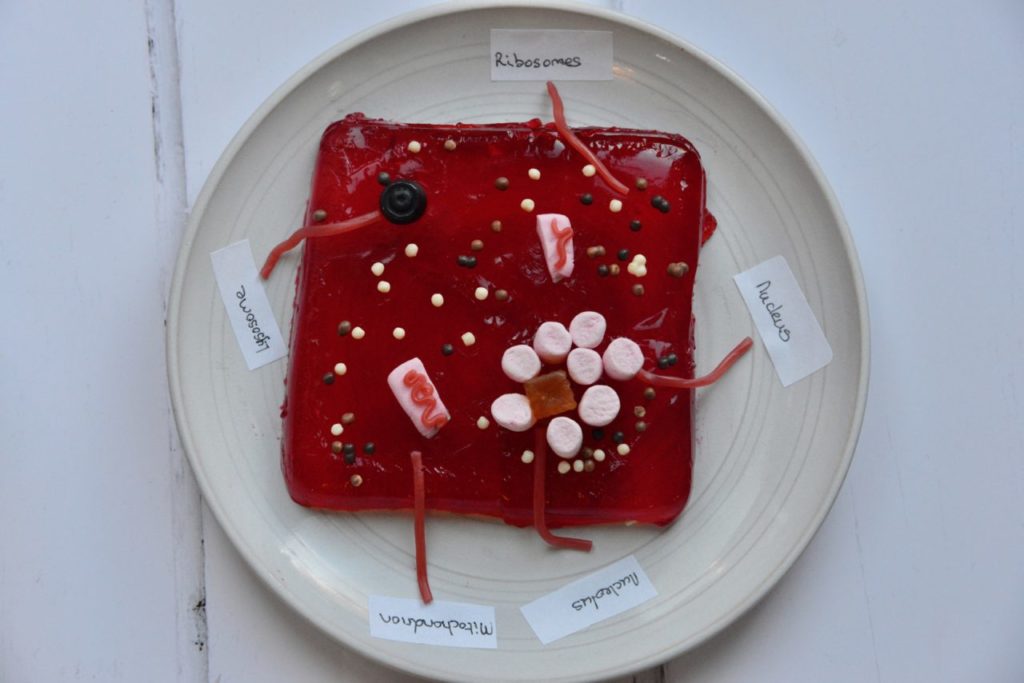
Discover the differences between plant cells and animal cells by making cell models.
The key differences are that only plant cells have a cell wall, large vacule and chloroplasts.
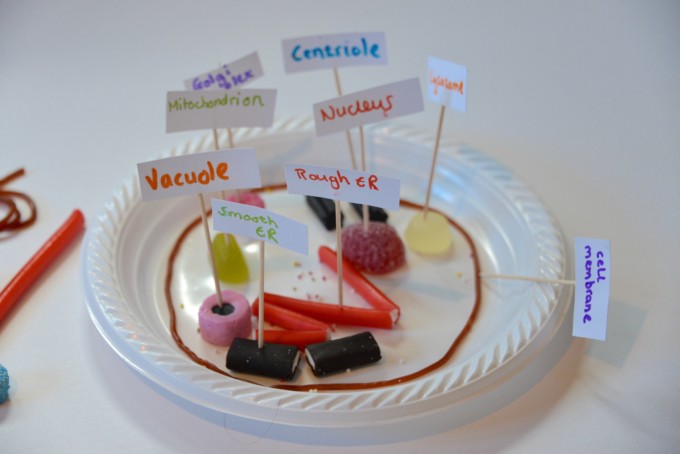




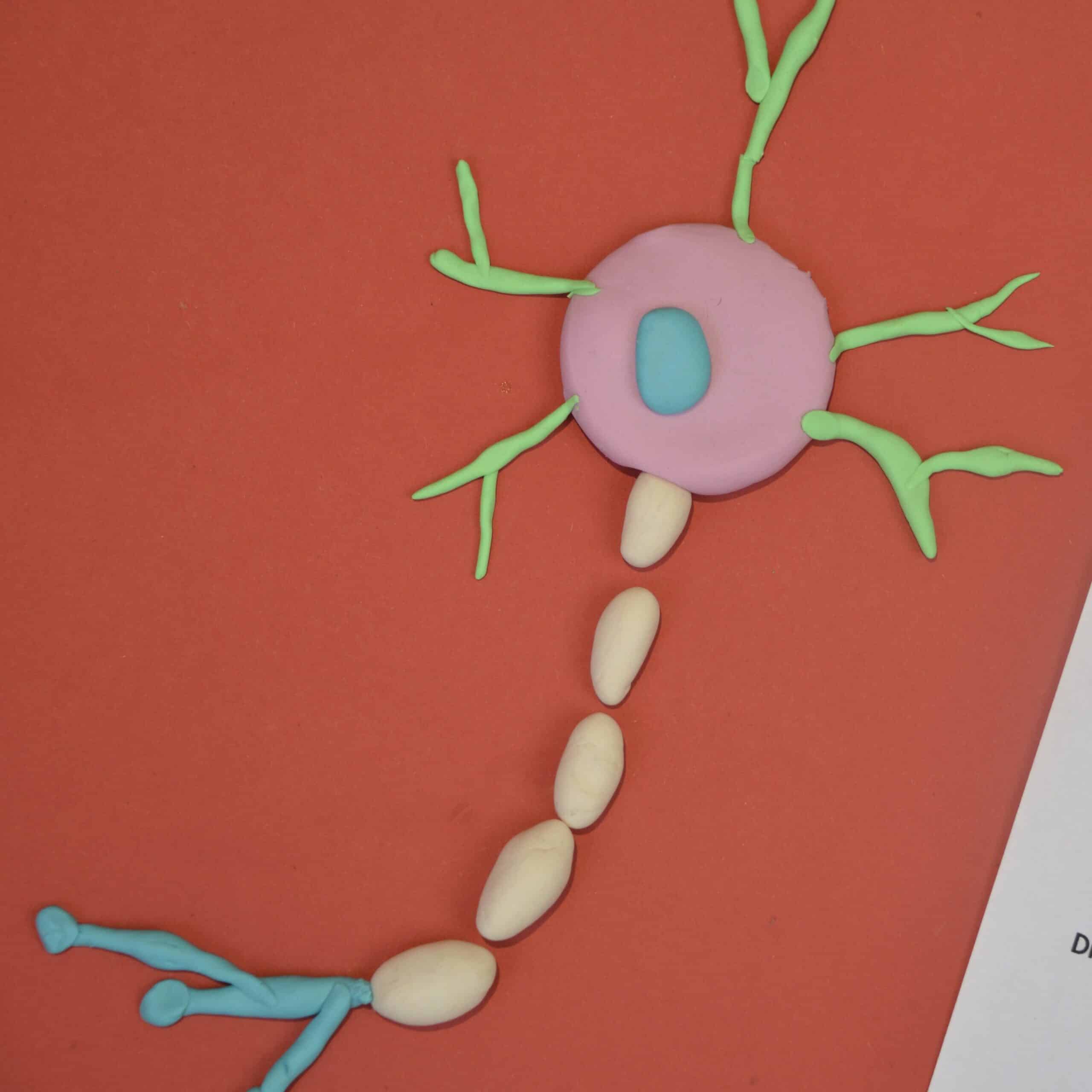
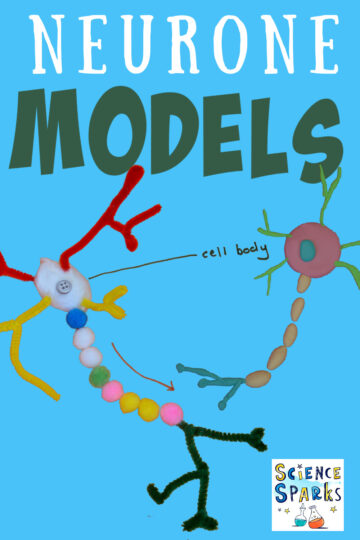
Make a model of a nerve cell. This is a fantastic activity for learning about how some cells are specialised for a particular function.
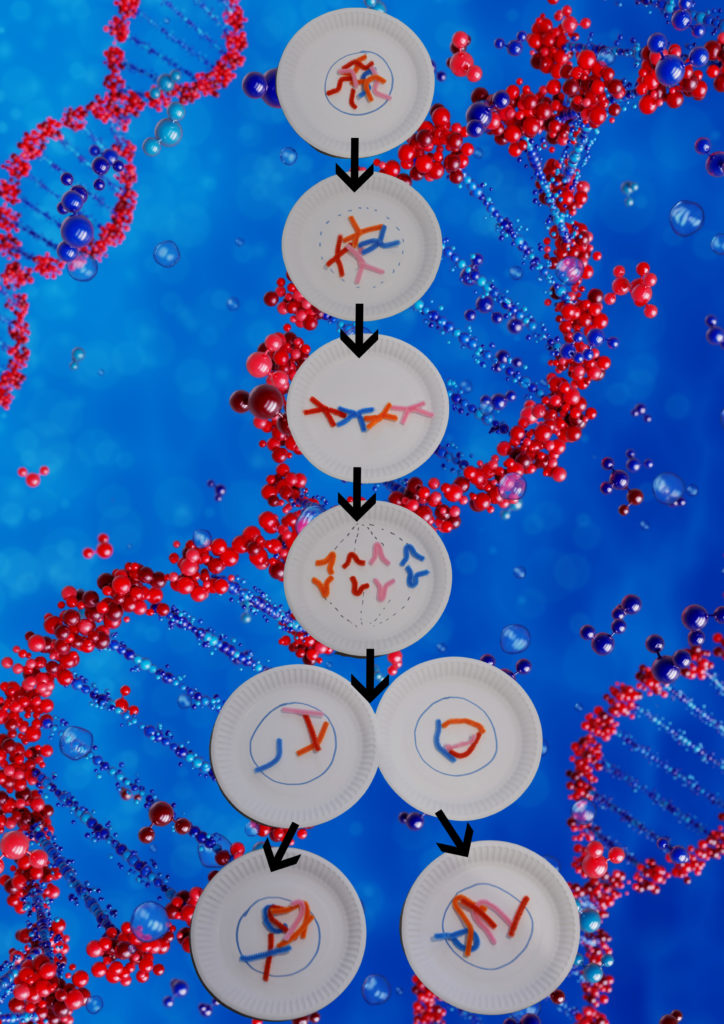
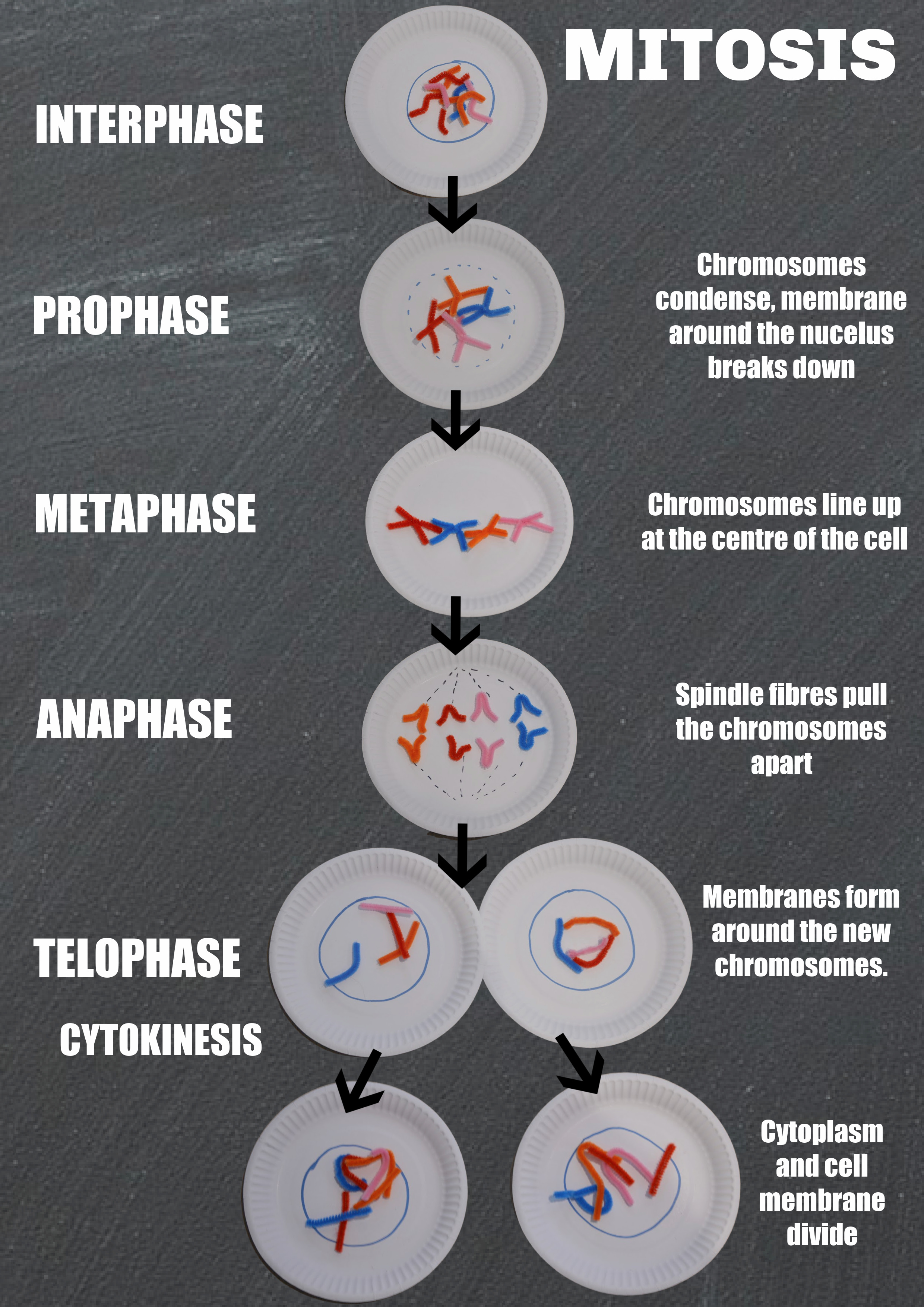
Paper Plate Mitosis
Cells divide by a process called mitosis. One fun way to visualise mitosis is using paper plates and pipecleaners.
As an extra challenge, try creating a stop-motion animation of the process.
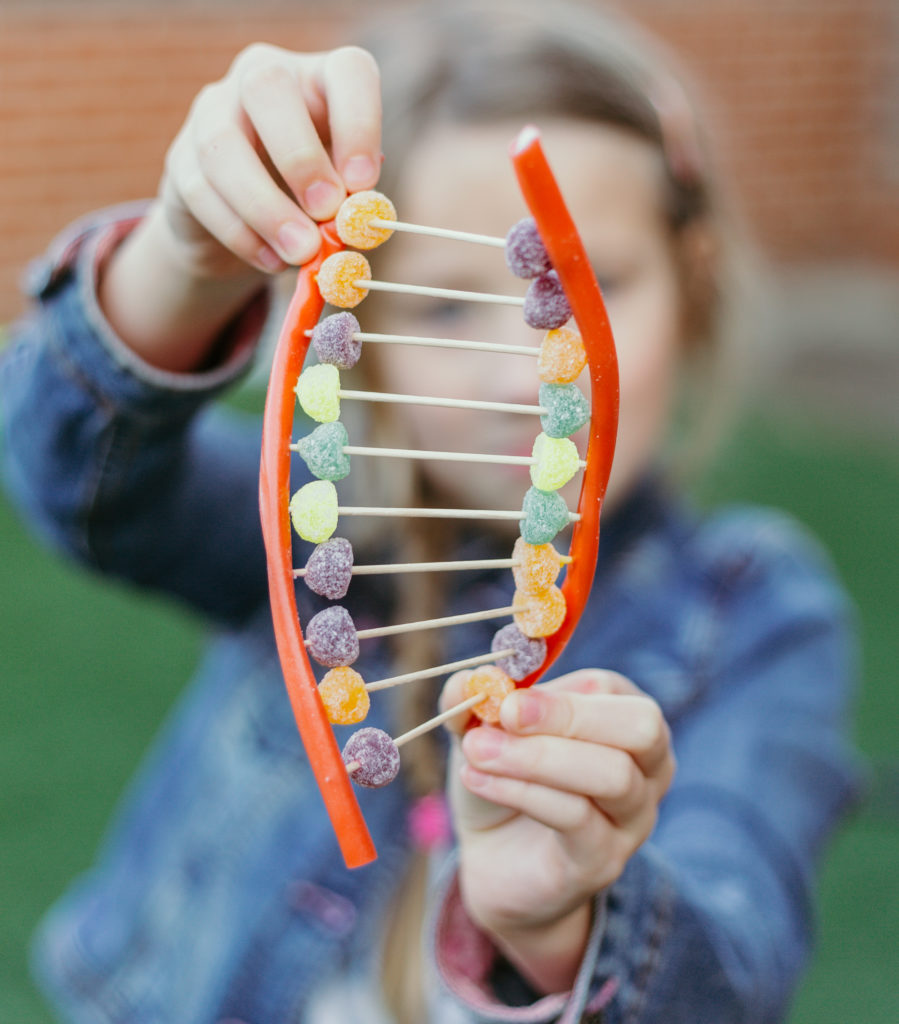
DNA Models
The DNA of a cell is found in an organelle called the nucleus. You can learn about the structure of DNA with a candy model showing the double helix structure.


Do you have any other fun ways to learn about cells?
Cells Quick Quiz
What is the basic unit of life?
The cell
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Which part of a cell is known as the 'powerhouse'?
Mitochondria
What three things does a plant cell have that an animal cell doesn't?
Large vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall
What type of cell is a bacterial cell?
Prokaryotic
Do bacterial cells have a nucleus?
No, DNA in a bacterial cell floats freely in the cytoplasm.
Give an example of a specialised cell
Nerve cell, red blood cell, egg, sperm, muscle cell
Last Updated on September 26, 2025 by Emma Vanstone


Leave a Reply