Fossils are the preserved remains of animals and plants that lived a long time ago.
Fossils can also be evidence of a prehistoric animal or plant, such as footprints or evidence of nests or burrows. These are called trace fossils.

Not all remains become fossilised. Fossilisation is actually quite rare. Most animal and plant remains decompose after they die ( or are eaten by scavengers), but if the remains are covered by sediment ( usually sand, mud or lava ), they may become fossils.
Stages of fossilisation
- The soft parts of the animal decompose, leaving the hard skeleton behind.
- Layers of sediment build up on top of the skeleton. As more and more layers build up, the pressure on the lower layers increases, and they start to turn into sedimentary rock.
- The animal skeleton dissolves as water passes through it. This leaves a gap in the layers of rock the same shape as the skeleton.
- Minerals from the water fill the gap left by the skeleton to form a replica of the original bone.
Quick Fossil Facts
Most fossils are of marine animals, as the seabed is the ideal place for layers of sediment to build up over a dead animal.
It takes thousands and sometimes millions of years for a fossil to form.
Fossils are forced up to the surface when tectonic plates collide, when ice sheets melt or can be pushed up as new rock forms beneath them.
The Latin word fossilis means dug up.
Fossilised animal poo is called coprolite and is very useful as it gives clues to what animals ate.
Weathering and erosion of layers of rock also allow fossils to be found.
Dinosaur fossils have been found on every continent.
Fossils have been found at the top of Mount Everest. This is because the Himalayas were formed when two tectonic plates collided, forcing heavier rock down and lighter rock upwards, making the top of the mountain home to 400 million year old fossils that were once at the bottom of the ocean!
A mould fossil is a 3D impression of an organism that has decomposed in sediment, leaving an imprint behind.
A cast fossil is when the mould becomes filled with organic material forming a replica of the original bone.
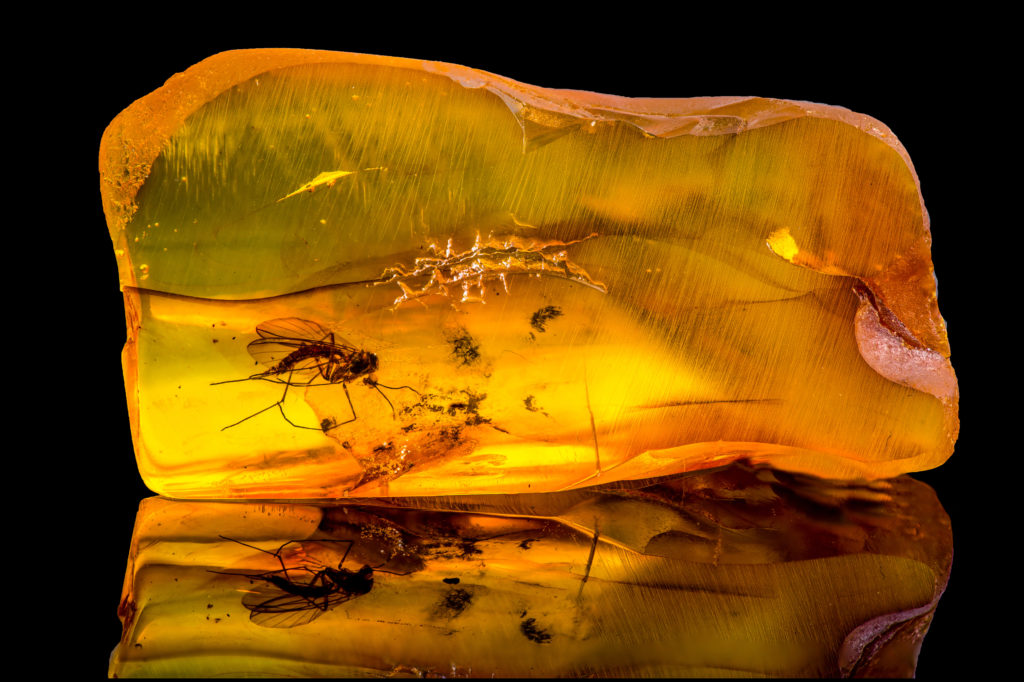
Animals can also be fossilised if they become trapped in amber, tar or ice!

Fossil Activity Ideas
Make a super simple fossil with clay. This is an example of a mould fossil.
Make a fossil of a Coelacanth.
Find out about the pioneering fossil hunter Mary Anning and make a model ammonite.
This gummy fossil activity from Teach Beside Me is fantastic too!
Finally, have a go at making your own mould fossil.


Last Updated on June 29, 2023 by Emma Vanstone



Leave a Reply