What is an emulsion? Two or more liquids that don't mix create an emulsion when one is added to the other. The properties of the new liquid are different to either of the liquids alone. Emulsions are a special type of colloid.
Liquids that don't mix together are called immiscible liquids.
Examples of Immiscible Liquids
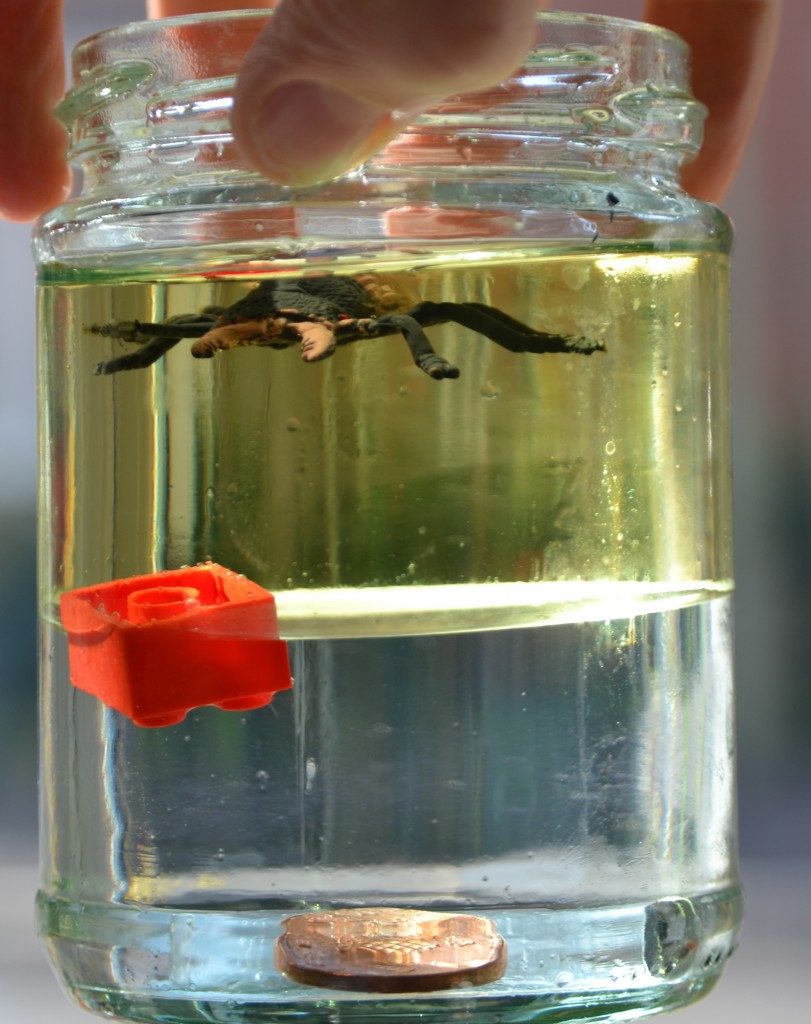
Oil and water are examples of immiscible liquids. This density jar shows how some objects float on the water layer and some on the oil layer.

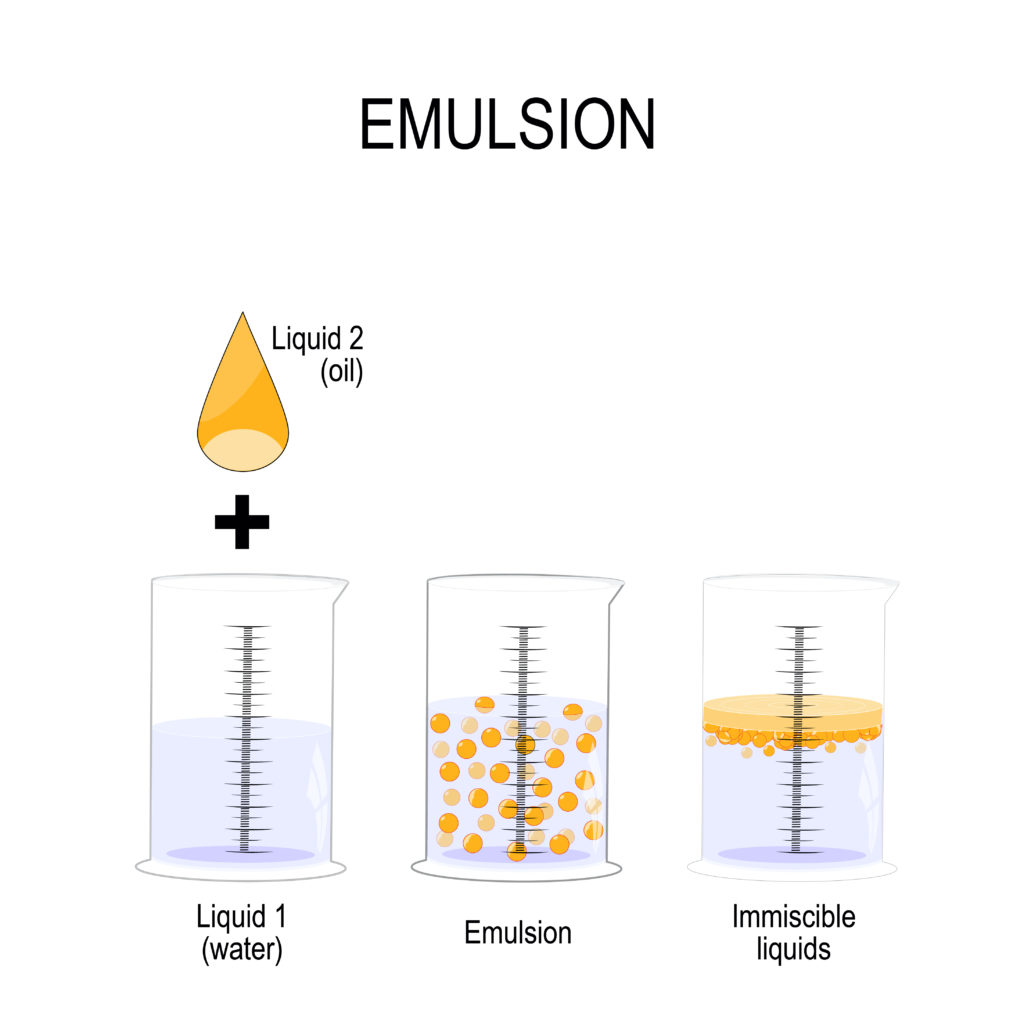
The diagram above shows the difference between a liquid, an emulsion and immiscible liquids.
You can see that in the emulsion, liquid two is spread evenly through the water.
What is an emulsifier?
Emulsifiers are substances which stop liquids in an emulsion from separating. Emulsifier molecules have two different ends. One end is hydrophilic (water-loving) and the other end hydrophobic (water-hating). In the case of oil and water, the hydrophilic end of the emulsifier forms a bond with the water and the the hydrophobic end forms a bond with the oil!
Emulsifiers are used in foods such as ice cream, sauces and biscuits to stop the oil and water from separating!
Examples of emulsifiers
Egg yolks are an example of a food emulsifier. It is egg yolks that stabilise mayonnaise and hollandaise sauce.
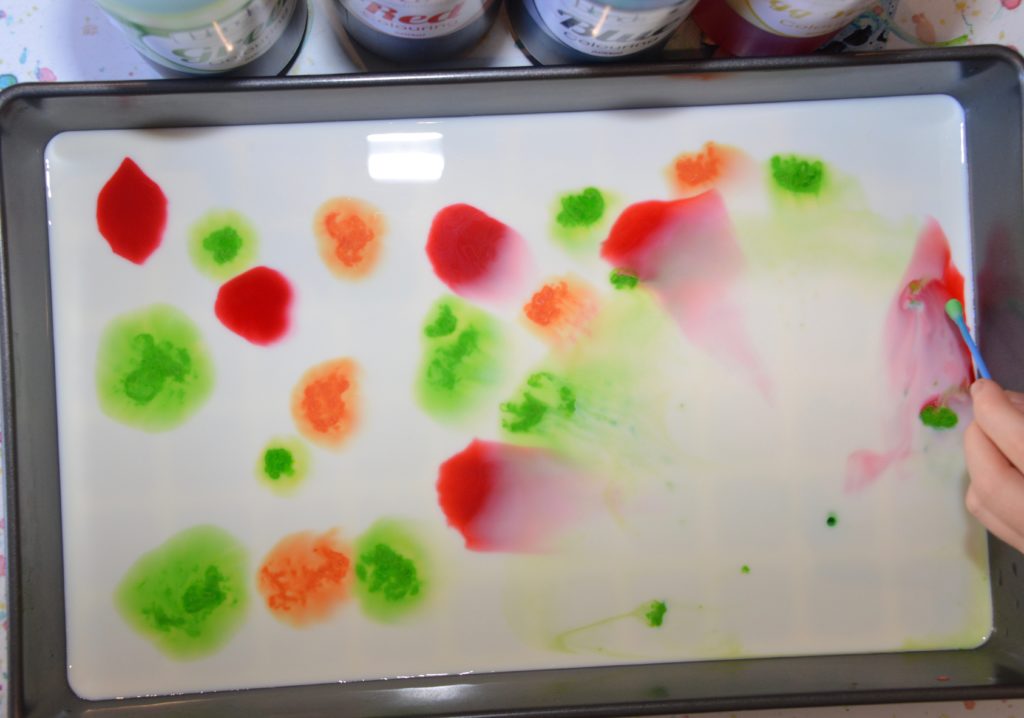
Find out more about emulsions with a magic milk experiment. This uses dish soap ( washing up liquid ) as an emulsifier.

Last Updated on January 11, 2023 by Emma Vanstone



Leave a Reply