My 10 year old is currently reading a book called 101 People Who Made History. When flicking through, I found myself naturally drawn to the many amazing famous scientists who have helped make the world what it is today with their hard work, sheer determination and passion for science and technology.
I’ve collected a few activities and simplified experiments linked to famous scientists to help children understand the concepts these inspirational people discovered.
Famous Scientist Experiments
Galileo Galilei (1564 to 1642)
Galileo was an astronomer, physicist, mathematician and inventor. He built his own telescope, which allowed him to discover features of the surface of our moon and the moons of Jupiter!
When Galileo was alive, many people thought that the Earth was at the centre of the Universe. Galileo explained that the Earth orbits the sun (also stated by Copernicus ), a theory that got him into lots of trouble with the church. You can demonstrate this easily using our Sun, Earth and Moon demonstration.
One of Galileo’s most famous observations was that two objects of the same size and weight hit the ground at the same time when dropped from the same height. This is because the force of gravity acting on both objects is the same. You can test this by dropping two identical water bottles from the same height. Empty one bottle and leave the other half full. You should find that if you drop them from the same height, they hit the ground at the same time.
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus was an astronomer born in 1473 who realised that the Earth orbits the Sun, an idea strongly opposed at the time.
Copernicus’s model, Heliocentrism, involves the Sun being motionless at the centre and other planets rotating around it. Copernicus’s ideas marked the beginning of modern astronomy.
Can you create a model of the solar system showing the planets orbiting the Sun, make a solar system magnet maze, or paper plate model of the solar system?
Leonardo Da Vinci
Italian Renaissance Man Leonardo Da Vinci created some of the world’s most famous art works, including the Mona Lisa and Last Supper, but he was not just an artist. Leonardo Da Vinci was also a scientist who studied anatomy, geology and flight. He kept journals full of drawings of the different subjects he was studying and often wrote his notes using a kind of shorthand he invented himself. He also mirrored his writing, writing from right to left.
See if you can mirror your handwriting…how hard is it? Use a mirror to help.
Caroline Hershel
Caroline Herschel was the first woman to discover a comet, the first woman officially recognised in a scientific position to receive a salary, and the first woman to receive honorary membership into Britain’s Royal Society.
She made a huge contribution to the field of astronomy in her lifetime, both independently and alongside her brother, William Herschel.
You can learn about the structure of a comet by making a simple comet model.
Isaac Newton
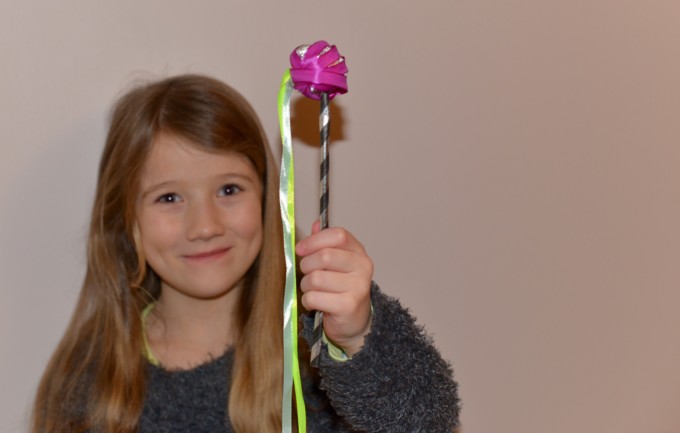
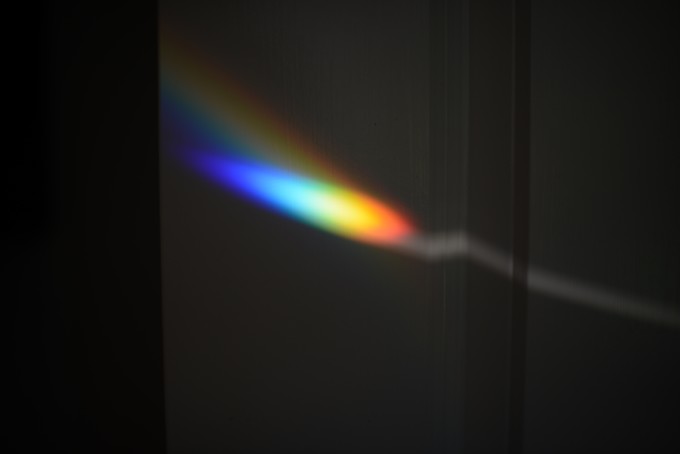
As well as figuring out why objects fall to the ground and why planets orbit the Sun, Isaac Newton showed that white light is actually made up of a range of colours and used a prism to show this. Did you know the Hubble Space Telescope is based on Newton’s reflecting telescope design?
You can split white light into all the colours of the rainbow by shining a torch through a prism in a dark room. Or, you can get the same effect by blowing bubbles outside. When white light shines through the film of the bubbles, it is reflected and dispersed, splitting white light into its different wave lengths and showing all the colours.
Isaac Newton also created the Laws of Motion. One brilliant way to demonstrate all three laws is to make a film canister rocket.
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin showed that life on Earth results from millions of years of gradual changes, a theory we call Evolution by Natural Selection. This means that animals best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and pass those features on to their offspring.
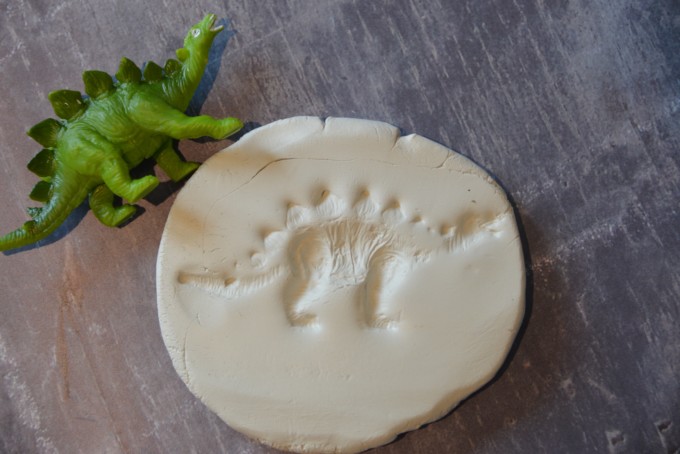
Darwin made many of his discoveries while on a 5 year voyage on a ship called HMS Beagle. He collected samples, fossils and made observations.
You can make your own fossils using clay and small toys.
This activity would also be great for learning about Mary Anning.
Mary Anning
Mary was a fossil hunter who helped find some of the first dinosaur bones. Mary’s work helped scientists form the theory of Evolution.
Mary faced many difficulties and obstacles in her life and career. She was from a poor family with no formal education, which meant she couldn’t join scientific societies or attend university lectures, and she wasn’t always fully credited for her findings.

Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French Chemist who found that bacteria cause harmful diseases. He also discovered that bacteria can be killed by boiling, a process we call Pasteurisation.
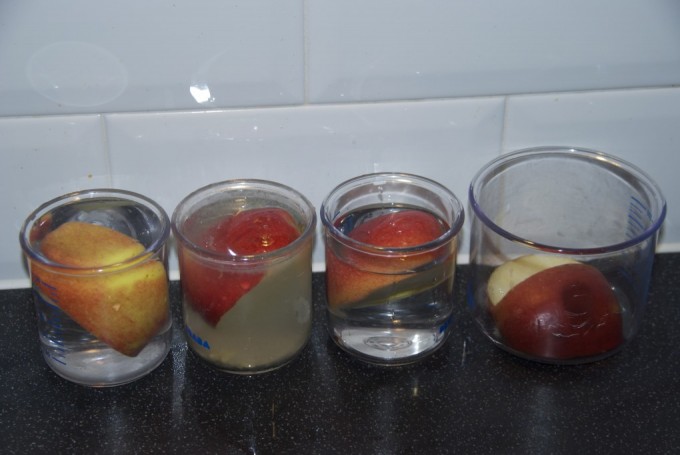
You can see the effect bacteria and other micro-organisms have on food by leaving them in different conditions and observing what happens. We placed apple segments in vinegar, salt, water, and air, and we got some interesting results.
Joseph Lister
Joseph Lister was a British doctor who believed that germs from dirty equipment and people not washing their hands were causing infections in patients after operations. He found that sterilising equipment and using antiseptics ( substances which prevent or slow the growth of microorganisms) drastically reduced the infection rate.
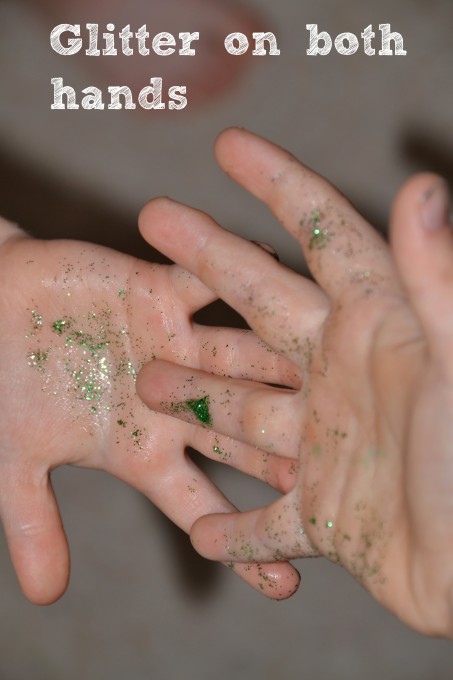
You can see how easily microorganisms spread between people by putting a little glitter and hand cream on your hand and then shaking hands with someone else. You should find that the glitter spreads to their hand, too. Keep shaking hands with people. How many can you infect with your glitter germs?
This is also a great activity to sit alongside, learning about Florence Nightingale.
Florence Nightingale
Florence is considered to be the founder of modern nursing. The soldiers she cared for during the Crimean War called her The Lady with the Lamp as she worked all night looking after them.
Florence was the first woman to be given the Order of Merit, the first woman to become a member of the Royal Statistical Society ( because of her skills with numbers and presenting data ), and the first woman to receive The Royal Red Cross.

Wilhelm Roentgen
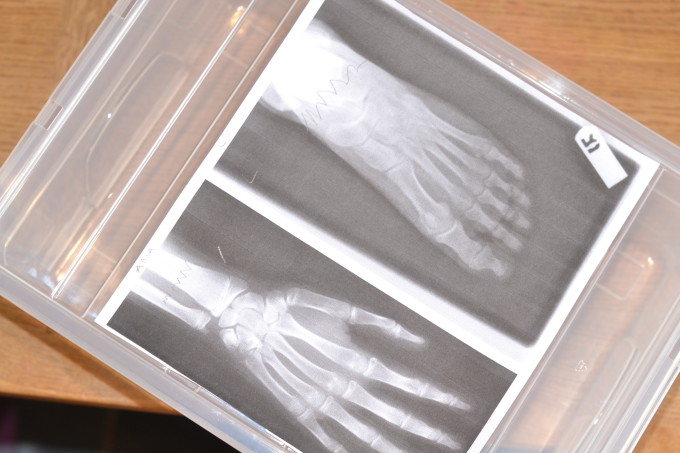
Wilhelm Roentgen was a German physicist who discovered X-rays. You can learn about X-rays and how they are used to detect broken bones with these easy bone themed science activities.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize. She discovered two new radioactive elements and realised that radiation could be used to treat human diseases. Marie used her knowledge to improve X-ray machines and created one small enough to fit in an ambulance.
Check out my Marie Curie Fact File and ideas for celebrating her achievements.
Ernest Rutherford
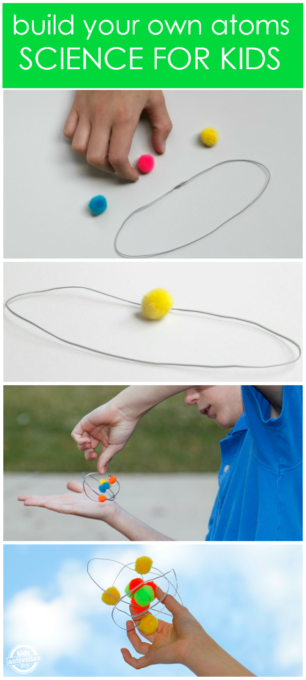
Ernest Rutherford discovered the structure of the atom, figuring out that most of an atom’s mass is at its centre ( nucleus ), with the rest being mostly empty space. Rutherford also found that the nucleus could be broken apart if struck by another high-energy particle. He created a new science known as nuclear physics.
Kids Activities Blog has a great activity that shows you how to make a model of an atom.
Watson and Crick
James Watson and Francis Crick worked together at Cambridge University studying the structure of DNA. They discovered that DNA ( Deoxyribonucleic Acid ) consists of two strands twisted together in a double helix.
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins also contributed to this groundbreaking discovery.
Did you know you can easily extract DNA from strawberries? Steve Spangler shows you how.
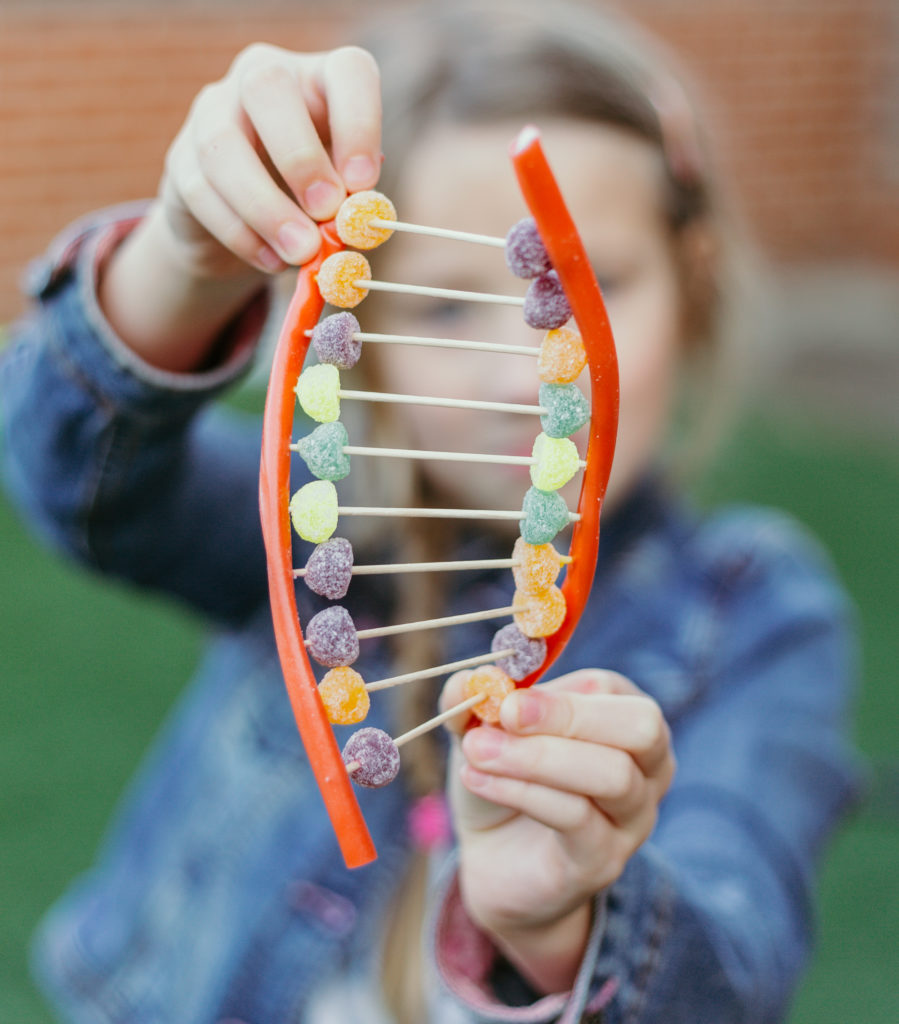
You can also learn about the structure of DNA with our easy candy DNA model.

Rosalind Franklin
Find out more about the inspirational Rosalind Franklin with my FREE Rosalind Franklin Fact File.

Ada Lovelace
Read more about the women who wrote the first computer program and try some simple coding with my free Ada Lovelace Fact File.
Marie M. Daly
Marie Daly was an American biochemist and the first African-American woman to receive a Chemistry PhD in the United States. Marie’s incredible work led to a new understanding of how diet affects the human circulatory system.
Download my Marie M. Daly Fact File and make a model of a pumping heart.

Cai Lun
Cai Lun invented paper in 105! He used the soft inner bark of a mulberry tree, bamboo fibres and water. After mixing, he poured the mixture over a cloth and let the water drain away. When the mixture dried, it left behind paper! The invention of paper allowed discoveries to be recorded and spread much more quickly.
The process isn’t the same as that invented by Cai Lun, but Babble Dabble Do has a great paper making activity you can try.
Archimedes
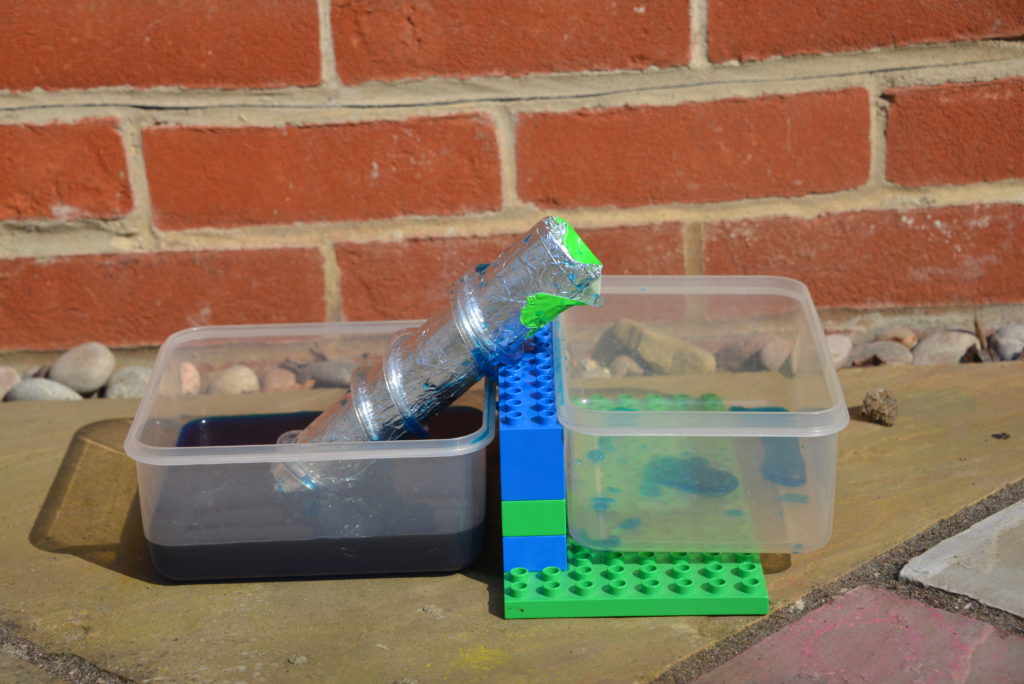
Archimedes was a brilliant mathematician, astronomer and inventor who lived in the 3rd century BCE. He worked out the value of pi, famously discovered that an object displaces its own volume of water in a bathtub and invented a simple pump machine that is still used today! One way to learn more about Archimedes is to make your own Archimedes Screw!


I’m going to keep adding famous scientists to this list, so do keep popping back.
Contains affiliate links
Last Updated on April 7, 2025 by Emma Vanstone










I’m a middle-grade teacher and just discovered this site. I LOVE IT!
Watson and Crink whilst given the credit for their DNA study, would not have got to their conclusions so quickly had it not been for Rosalind Franklin. Dr Franklin had her photo of DNA stolen by her lab partner (Maurice Wilkins) who then partnered with Crink and Watson. Photo 51 was taken in 1952. Watson and Crink published their DNA model in 1953 thanks to the help of Franklin’s now famous photo. Franklin died of cancer in 1958 never knowing that her photo had been stolen. Watson, Crink and Wilkins won their 1962 Nobel Prize because of her help but sadly she was never recognized for her contribution.
my kids are only 3months old and 17 months old and im already looking for ways to get them into science. Thank you so much!