Biology is the study of life and living things, including plants, animals and microorganisms. Biologists refer to living things as organisms. This collection of biology experiments for kids covers some of the most important concepts in biology
There are many different branches of biology, including:
Ecology - the relationships between organisms
Zoology - the study of animals
Taxonomy - classification of organisms
Anatomy - the structure of organisms
Botany - the study of plants
Microbiology - the study of tiny organisms
Physiology - functions of living organisms
Biology is a vast and exciting area of science covering everything from the smallest virus to evolution, ecosystems and the climate.
Top 10 Biology Experiments for Kids
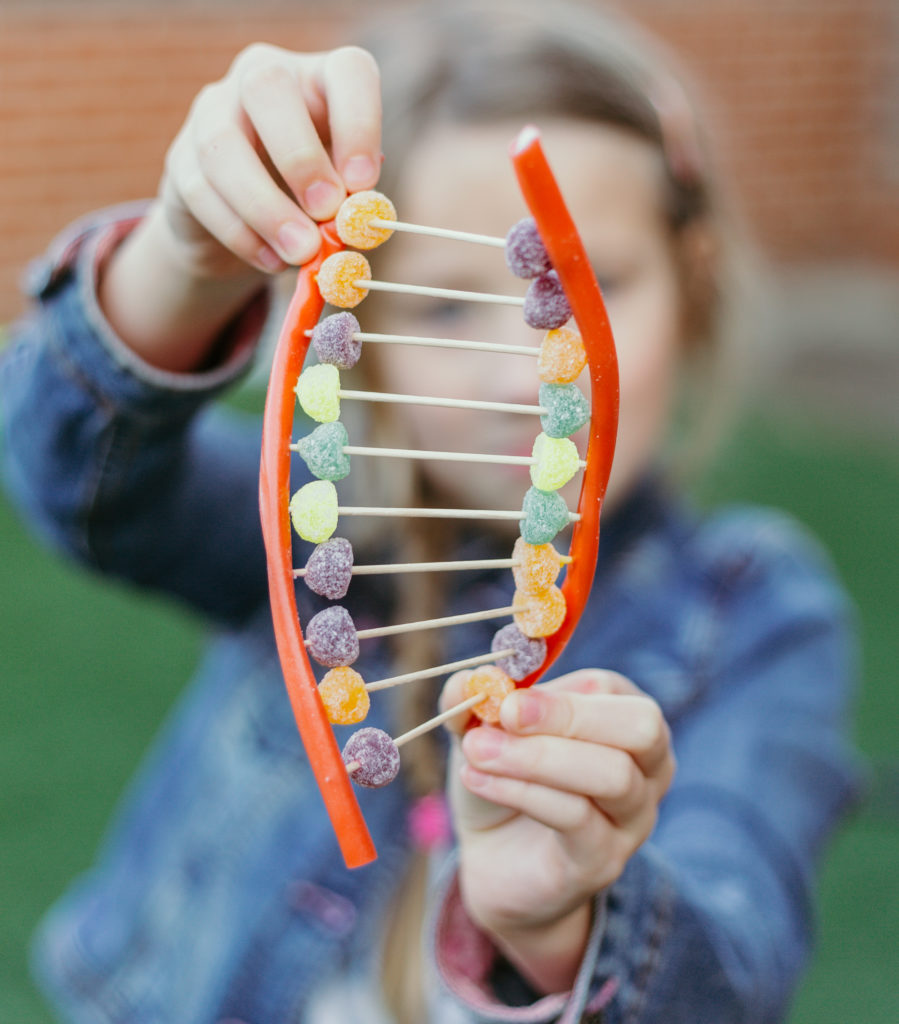
1. Candy DNA Model
This candy DNA model is a great way to learn about the double helix structure of DNA and tastes great, too!

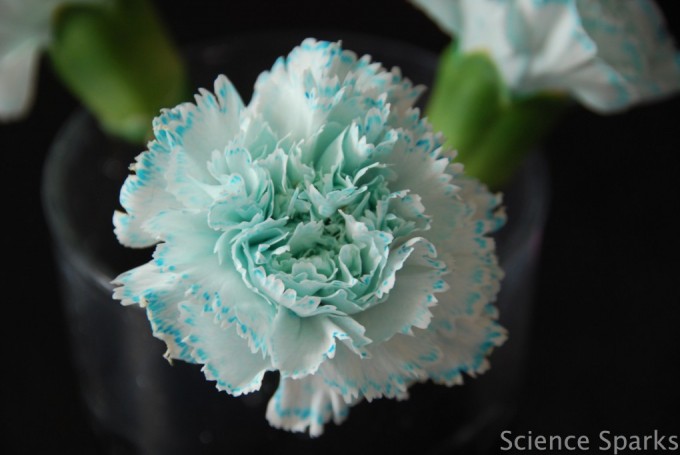
2. Colourful flowers - transpiration investigation
Place white flowers in a pot of food colouring and water to change their colour. This activity is a brilliant visual way to learn about transpiration and transport in plants.

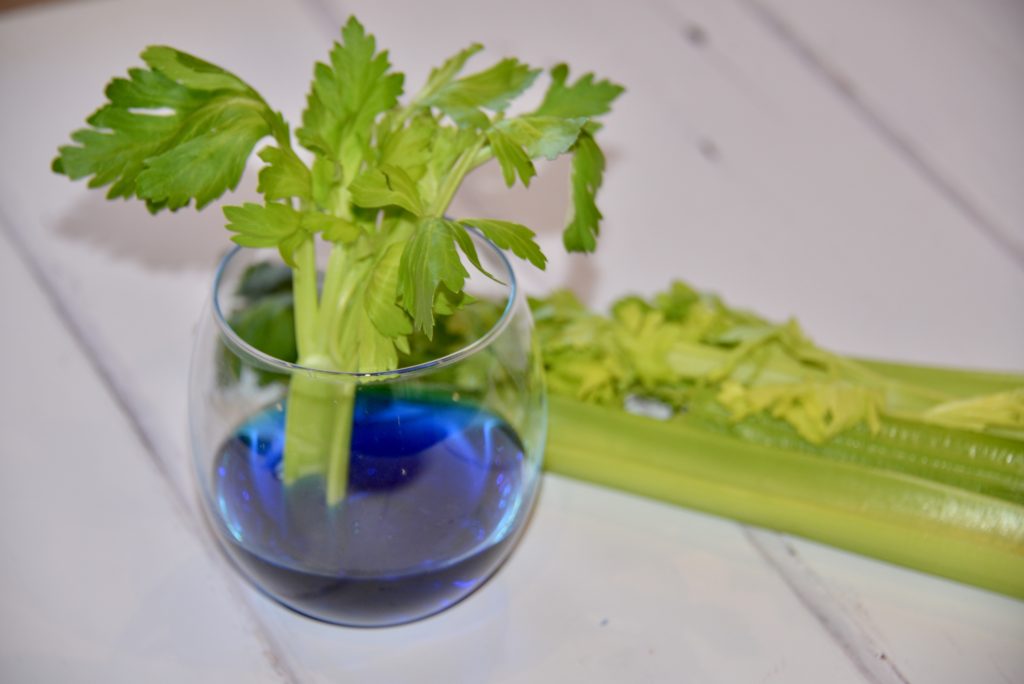
3. Investigate the effect of increasing temperatures on transpiration
Use celery and food colouring to find out how increasing temperature affects the rate of transpiration in plants.

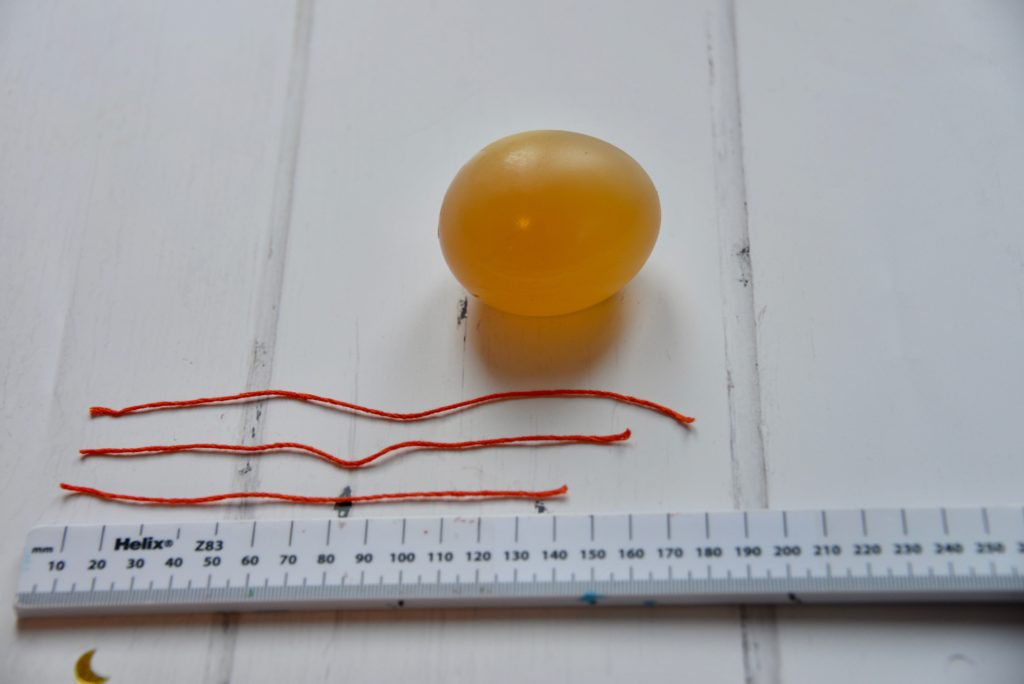
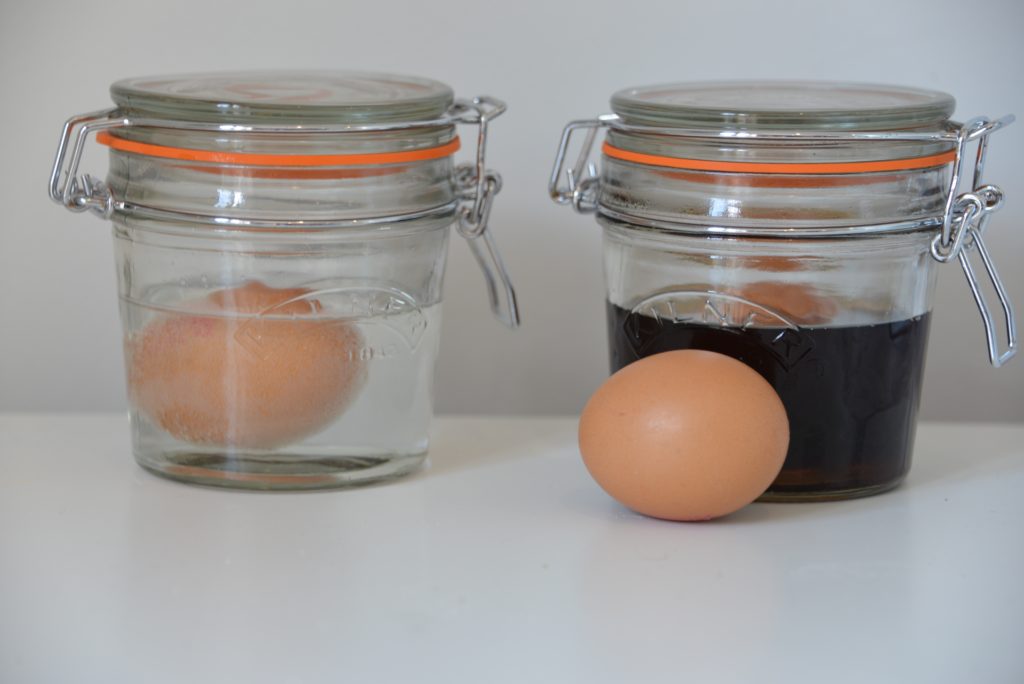
4. Osmosis and eggs
Learn about osmosis with an egg without a shell. The shell is removed by soaking the egg in vinegar. Place the egg in water and watch it grow in size as water moves into it.
This is a fantastic visual way to demonstrate osmosis that always makes a big impact.

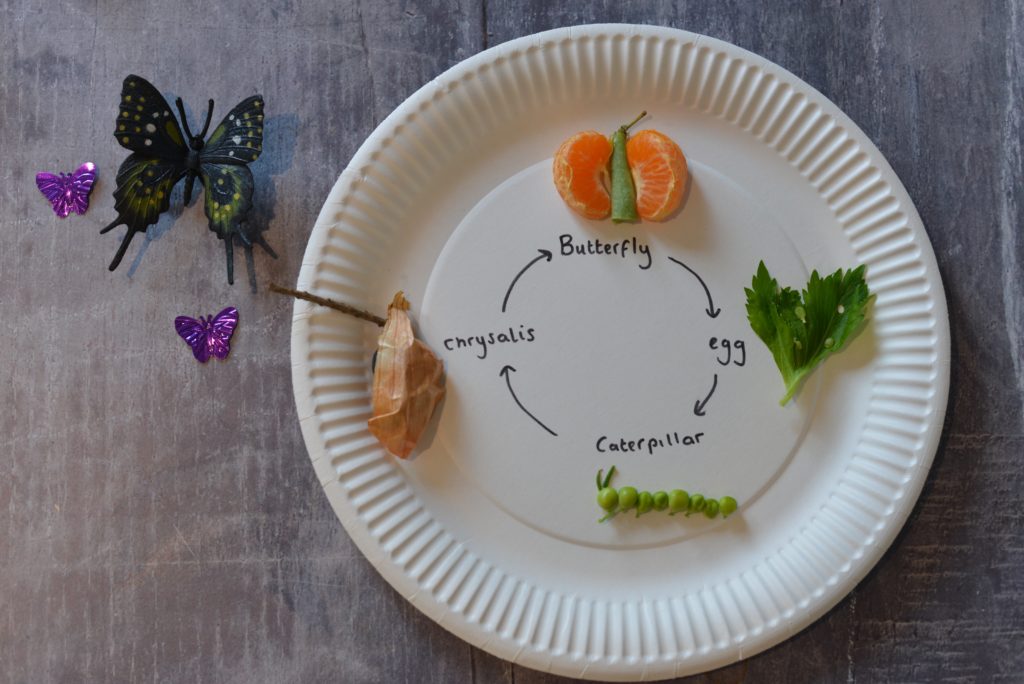
5. Edible butterfly life cycle
Make an edible butterfly life cycle using fruit, vegetables, pasta or sweets.

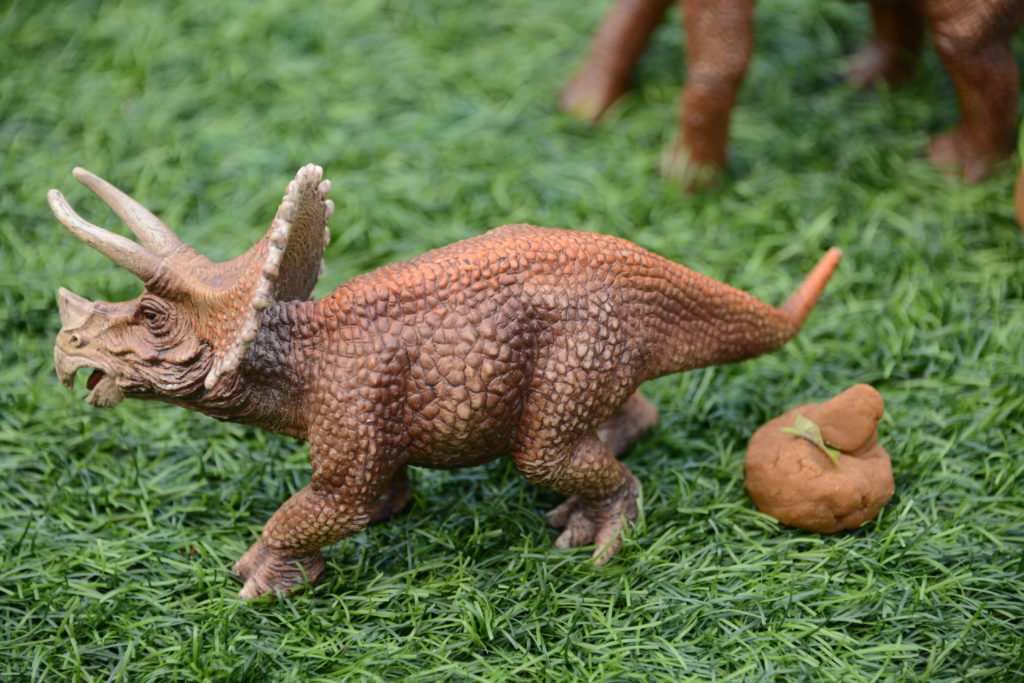
6. What Did Dinosaurs Eat? – Dinosaur Poop Investigation
Discover what dinosaurs ate with a fun dinosaur poo investigation! This is a wonderful activity for younger children who love searching through the playdough for clues to what dinosaurs ate.

7. How does exercise affect heart rate?
Find out how exercise affects heart rate with a simple investigation where children measure their heart rate before and after exercise.
8. What are teeth made from?
Use eggs to find out what teeth are made from and discover the food items that cause them to stain or decay.

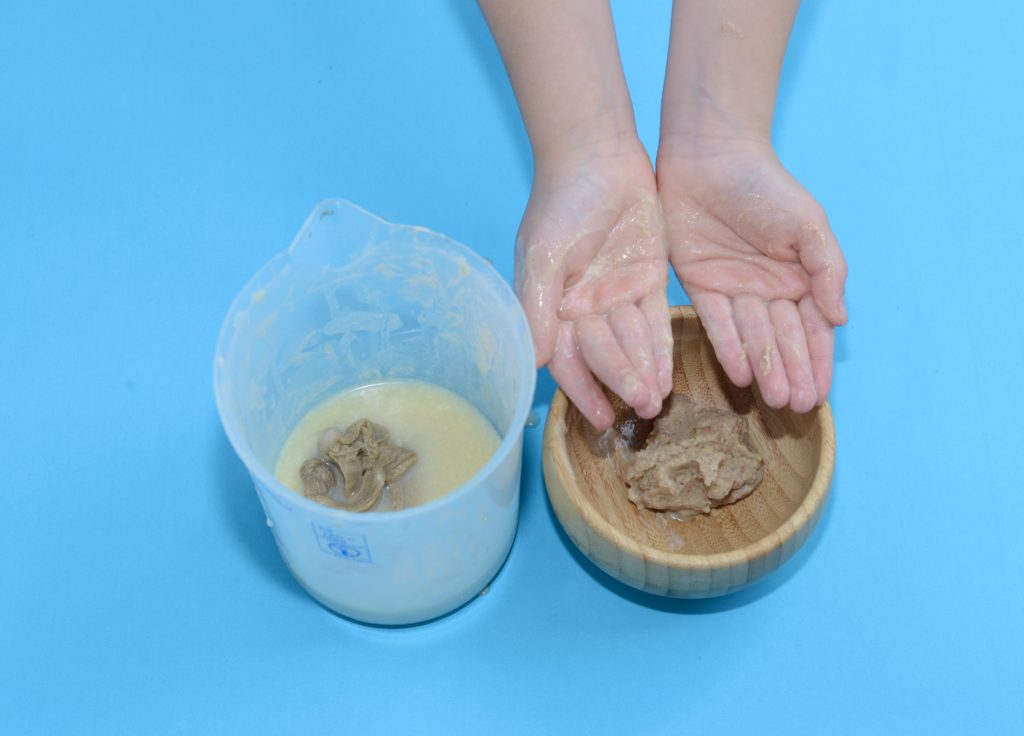
9. Digestive system model
Model the digestive system with biscuits, orange juice and tights. This is a slightly gross activity that kids of all ages will love.

10. Make a model lung
Find out how lungs work with a DIY lung model made from a plastic bottle, straw and balloon.
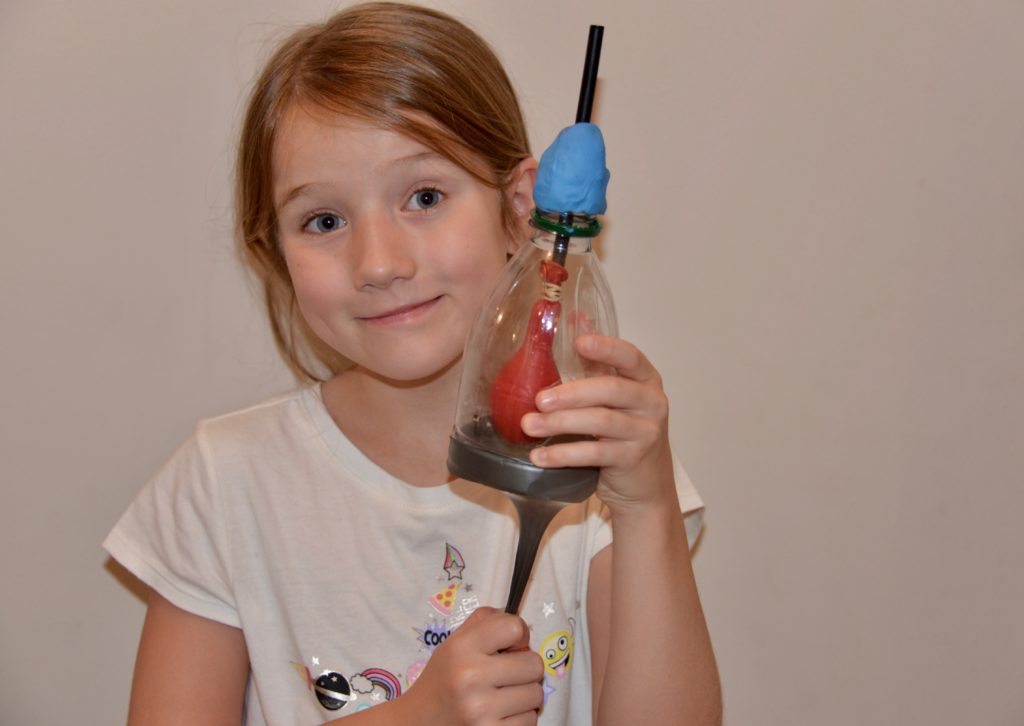
That's my personal top 10 biology experiments, but there's plenty more! Learn about water, cells, plants, enzymes and surface tension with the activities below.
All about Water
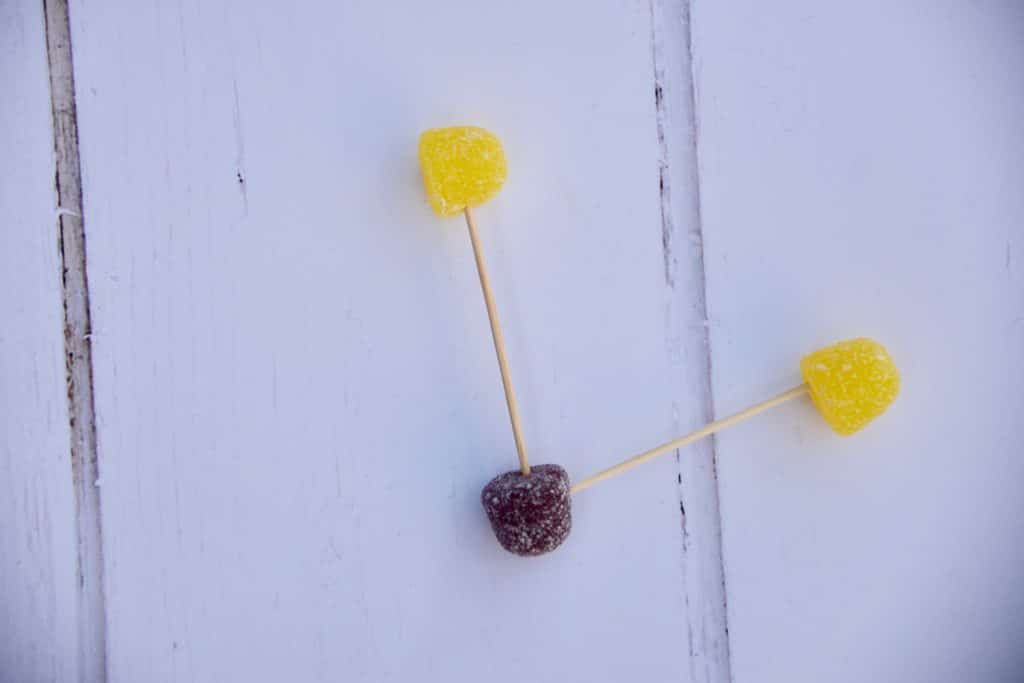
All living things need water; luckily, the Earth has a lot of water! Water is made up of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. This edible model of a water molecule shows the structure.
The yellow sweets represent hydrogen, and the purple sweet represents oxygen. The formula for a water molecule is H2O.

Water is a polar molecule. It has a positive end and a negative end. The negative end of one water molecule is attracted to the positive end of another water molecule, resulting in a hydrogen bond between the two molecules. This attraction between water molecules means water has a high surface tension. There are lots of simple ways to demonstrate surface tension. An investigation using a bowl of water with pepper sprinkled over the top is good to start with.
Surface Tension Demonstration
You'll need
A bowl of water
Ground black pepper
Washing up liquid ( dish soap )
Instructions
Fill the bowl almost to the top with tap water.
Sprinkle black paper over the surface.
Place a drop of washing-up liquid in the centre of the water.
The pepper should move very quickly to the sides.
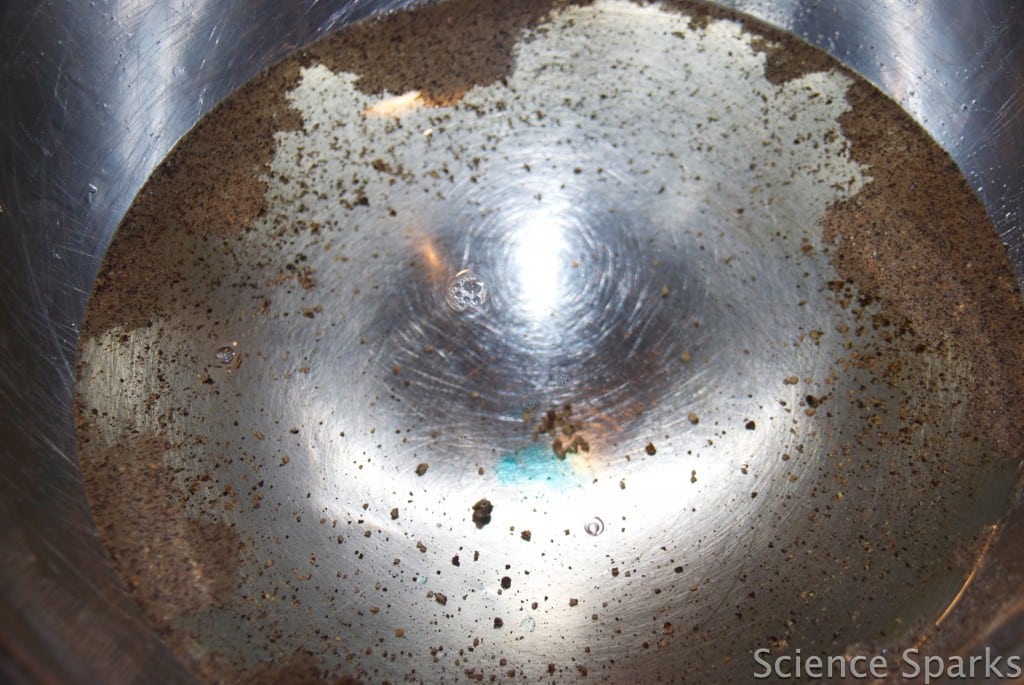

How does it work?
The washing-up liquid reduces the surface tension of the water, which allows the water particles at the surface to spread out, taking the pepper with them!
More surface tension demonstrations
Find out how many drops of water you can fit on a coin with Rookie Parenting.

Use surface tension to make lollysticks move in water.
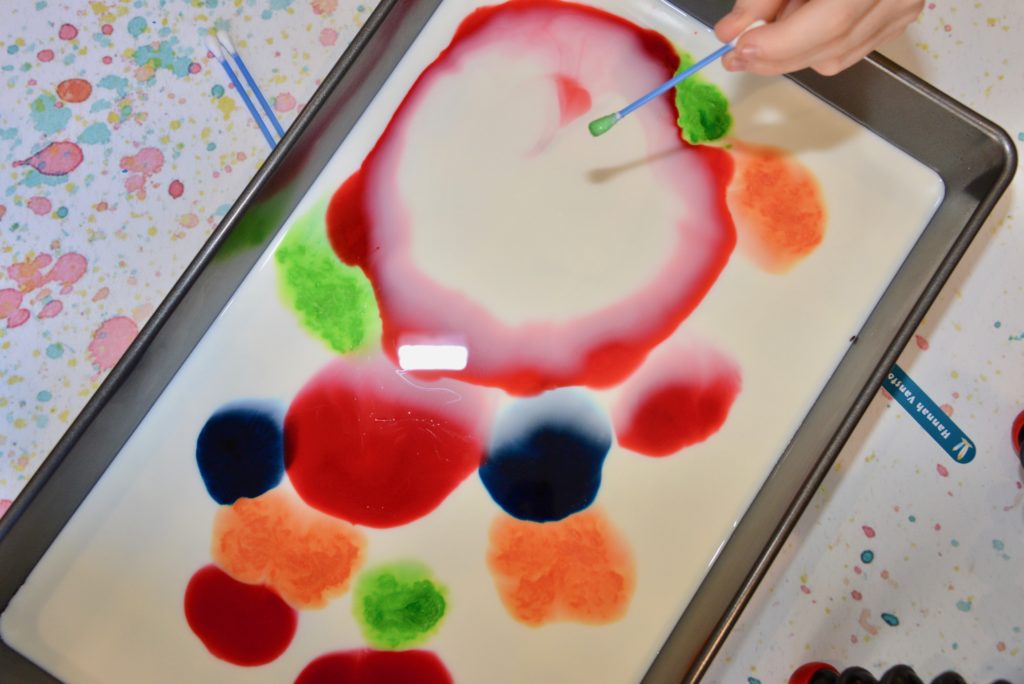
Try the classic magic milk experiment. Adding dish soap makes food colouring in milk explode with colour!

Enzyme Demonstrations
Organisms use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts. The easiest way to learn about enzymes is to use them! A microorganism called yeast is used in bread making as it contains enzymes that convert sugar and starch ( from the sugar and flour in the bread mix ) into carbon dioxide and ethanol. The carbon dioxide gas makes the dough rise. Giving bread the light, airy texture we all enjoy.
Enzymes only function in the right environment for them, which is different for different enzymes. Yeast needs warm, moist conditions, which is why bread dough is left somewhere warm to rise before baking.
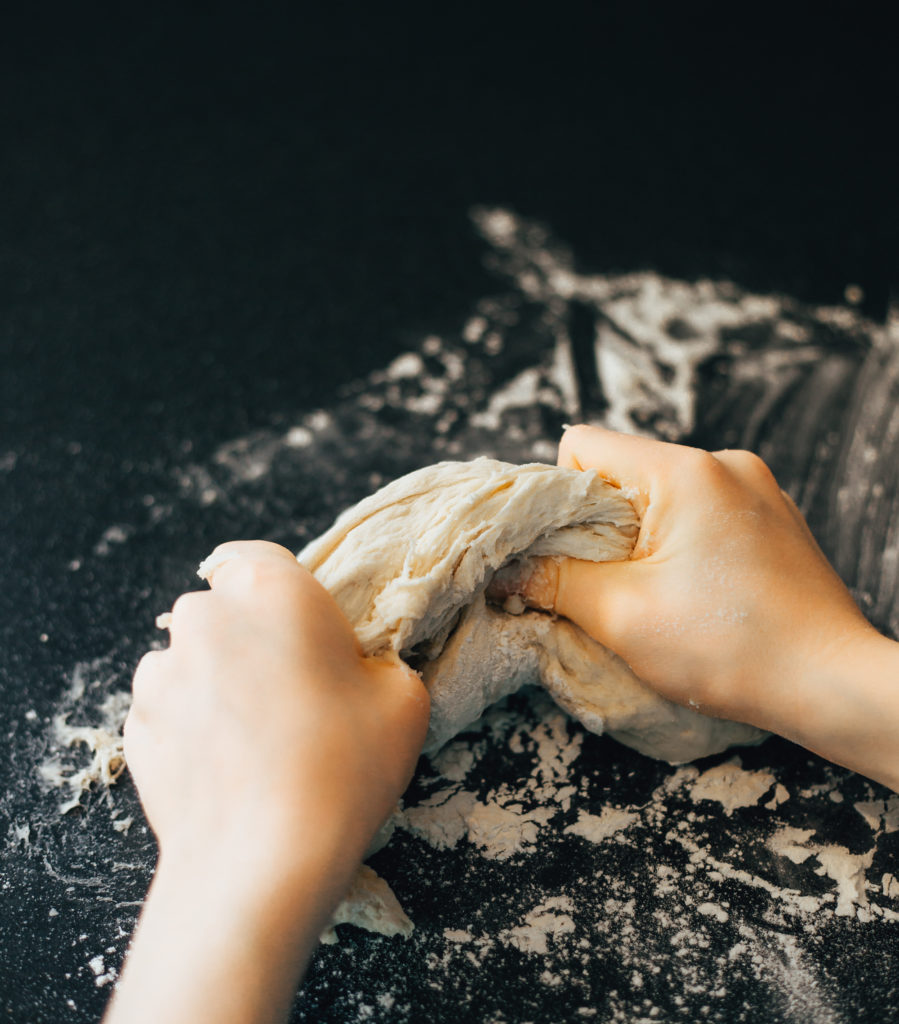
Learn about enzymes with pizza or bread dough
You can learn about the enzymes in yeast by making pizza or bread dough! If the dough is left somewhere cool, it won't rise as much as dough left in a warm place, as the enzymes in the yeast won't work as well.

Cell structure and function activities
All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
Bacteria and protozoa are examples of single-celled organisms.
A group of cells working together is called a tissue. Many tissues working together are an organ.
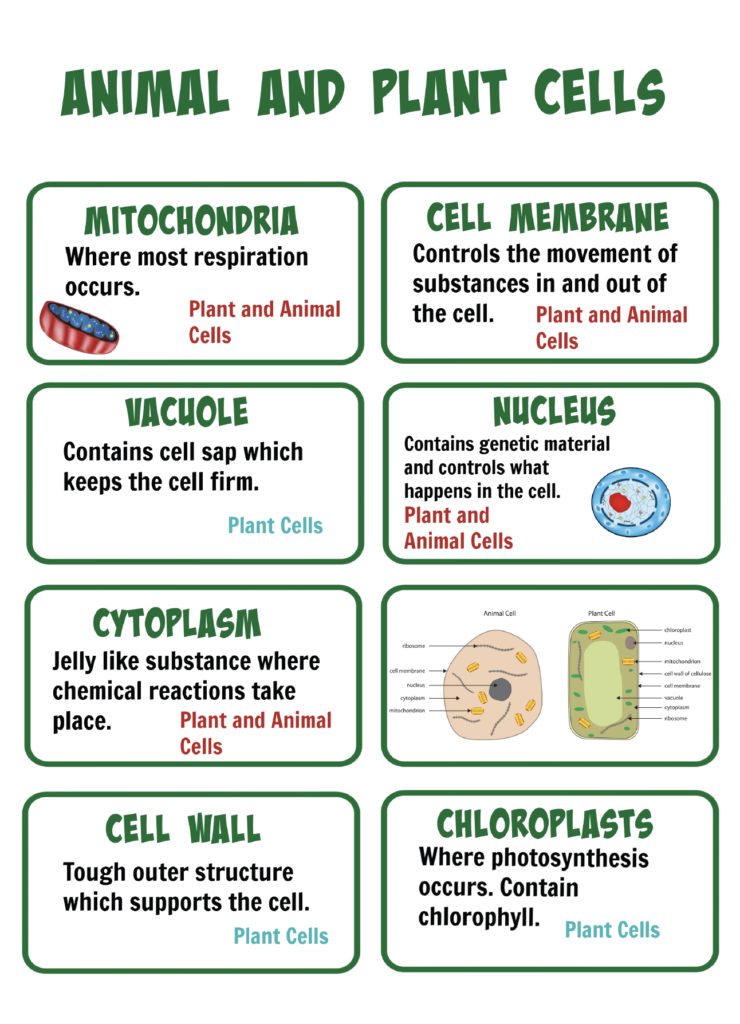
Cells contain organelles, which allow them to function.
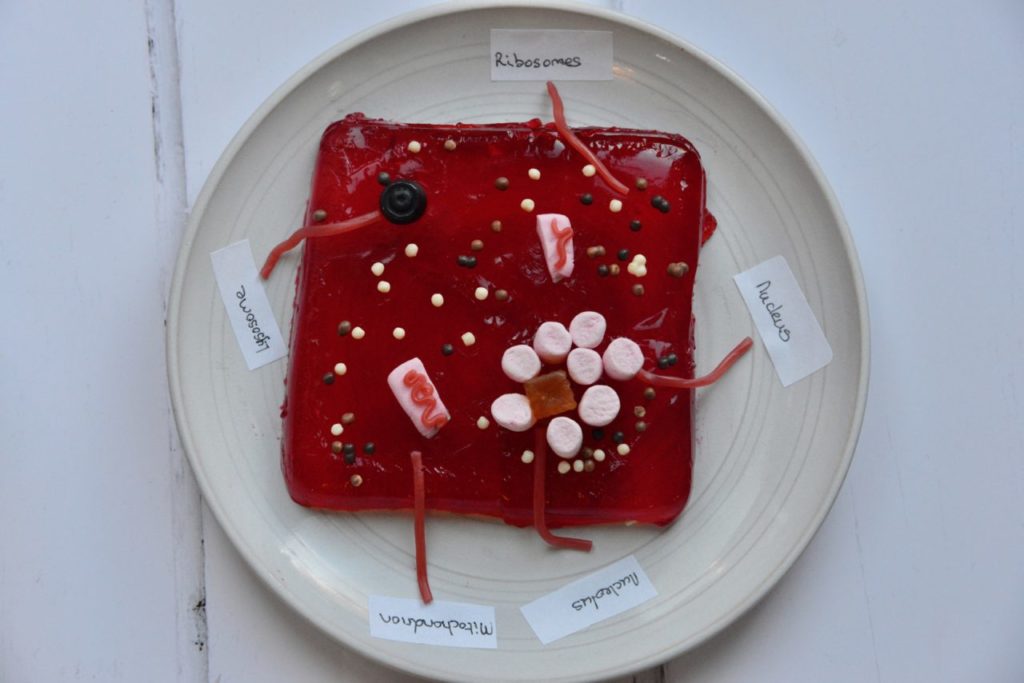
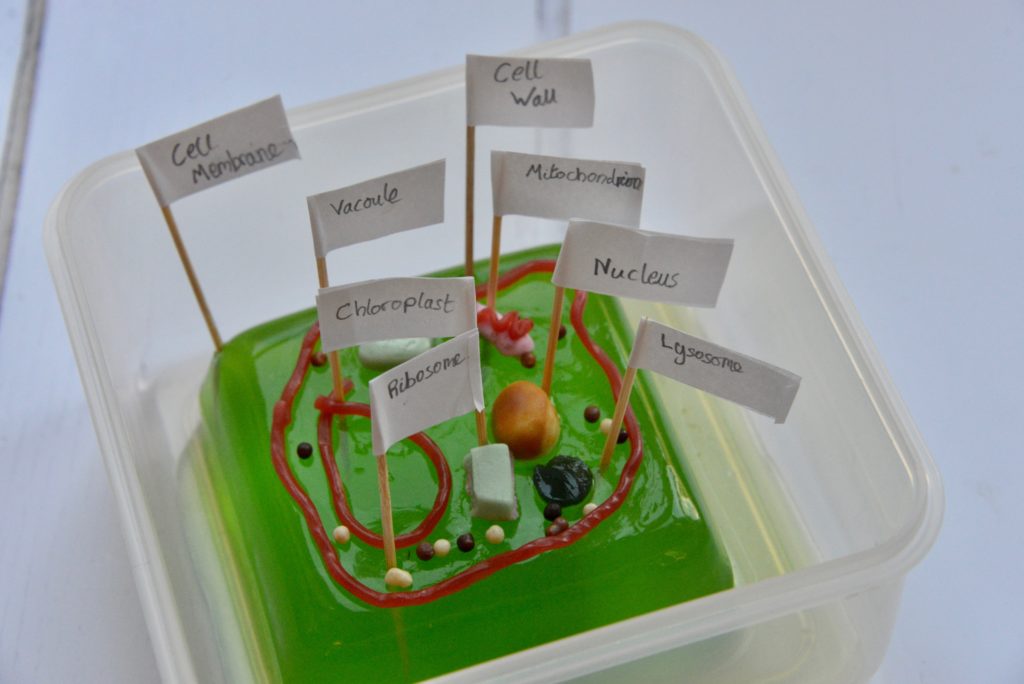
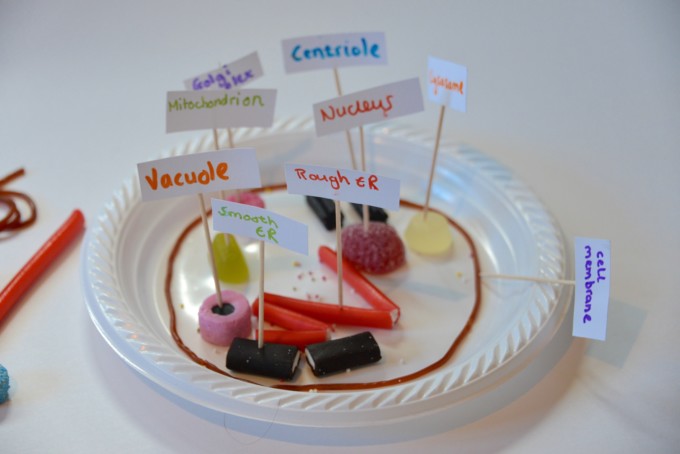
Plant cell models
Making a cell model is a fun way to learn about cell structure.
You'll need
Jelly/jello or a plate
Candy/sweets
Instructions
Make your jello as per the instructions in a lightly greased container.
When the jello is set, gently tip it into the container in which you want to make the cell.
Add sweets to look like each organelle.
Use toothpicks and stickers as signs to label the cell model.
Another idea is to combine this activity with the pizza dough to learn about enzymes and create a pizza model of a cell!



Learn more about cells, organelles and the difference between animal and plant cells with my animal and plant cell revision cards.
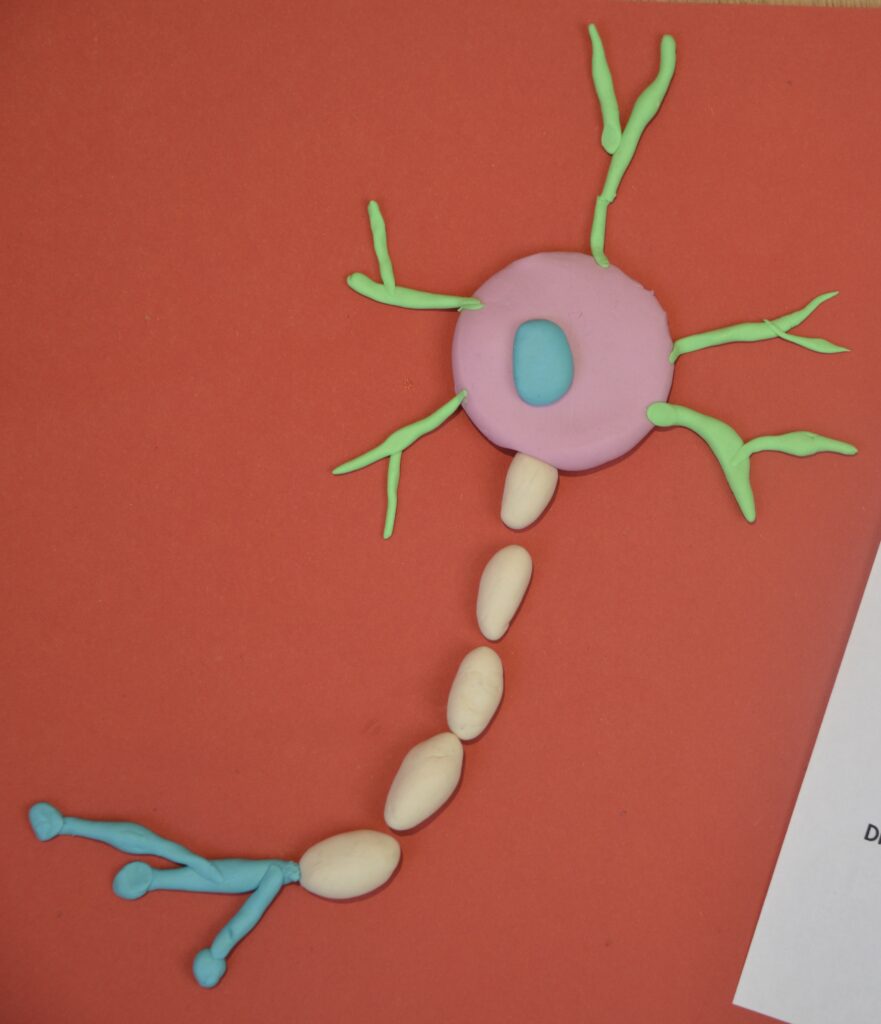
Specialised cells
Find out about specialised cells with a 3D model of a neurone cell.
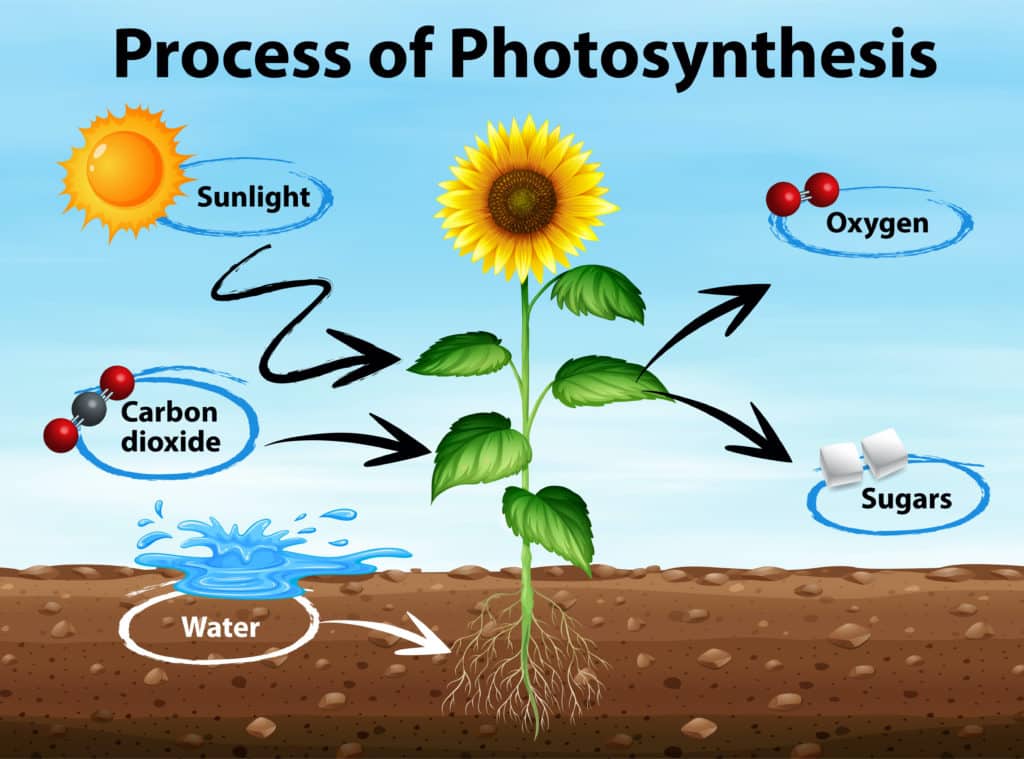
Photosynthesis Experiments
Photosynthesis is the process by which organisms ( mostly plants ) create energy. It occurs in organelles called chloroplasts.
Carbon dioxide + water (and light ) ———> glucose and oxygen
The energy for the reaction comes from sunlight. Photosynthesis is an essential process for life on Earth. It creates oxygen and also helps to remove the carbon dioxide created by human activity.
Plants use the glucose made during photosynthesis for cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis demonstration
Science Buddies have a great photosynthesis investigation you can try.
Plant structure and function
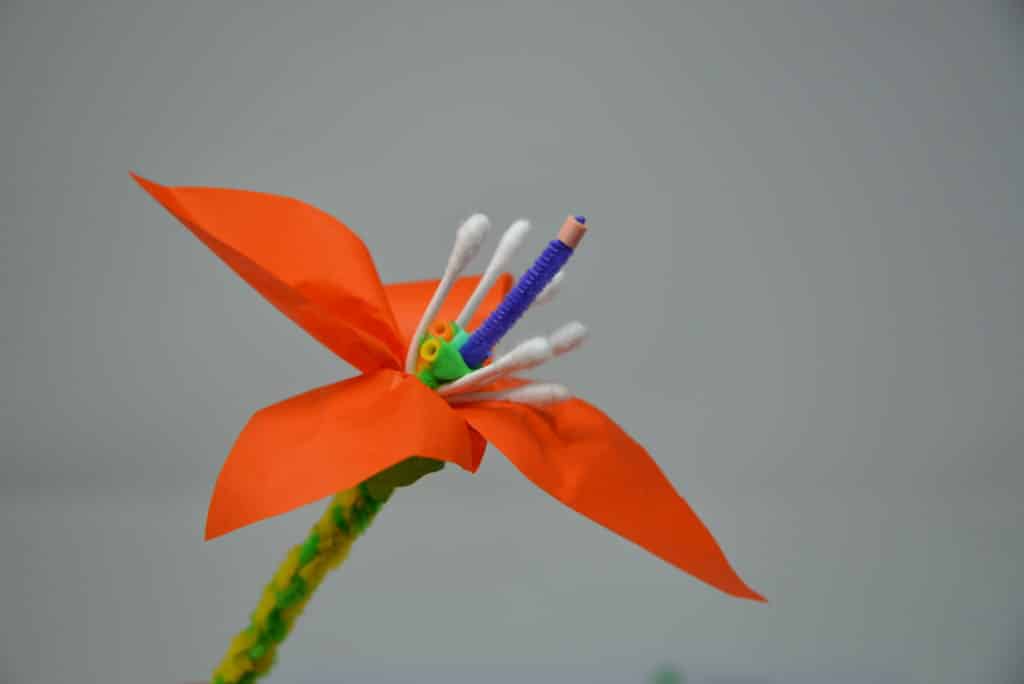
Dissect a flower
Dissecting a flower is a great way to learn about the different parts of a plant and their function.
You'll need
Any flowers with large parts - lily, daffodil, tulip
Magnifying glass
White card
Tweezers
Scissors
Instructions
Lay the flowers out on a table. Try to identify the different parts.
Label areas of the different parts of a flower on a sheet of white card or paper plate and match the dissected pieces to the correct label.

Another easy way to learn about plant structure and function is to make a 3D flower model.

Osmosis Experiments
Osmosis can be a tricky concept to get your head around as it is the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration. This can be demonstrated using an egg!
You might be wondering how on Earth an egg with a shell can be used to demonstrate the movement of water, and you're right to wonder. The first thing you have to do is remove the shell by soaking the egg in vinegar. The eggshell dissolves, leaving the semi-permeable membrane behind.
You'll need
Two eggs
Containers big enough to hold an egg
Vinegar
Water
Sugar
Instructions
Soak an egg in vinegar for 24 hours. Carefully remove the egg and rinse. You should be able to remove most of the shell. Leave it in vinegar for another 24 hours and then rinse again.
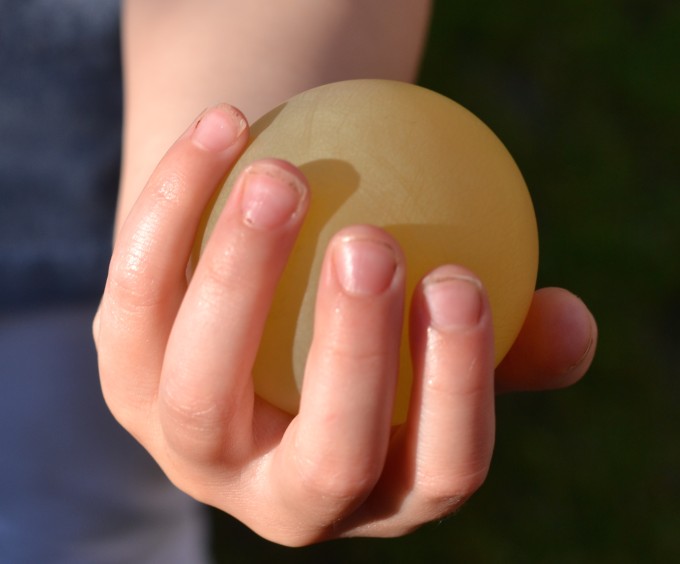

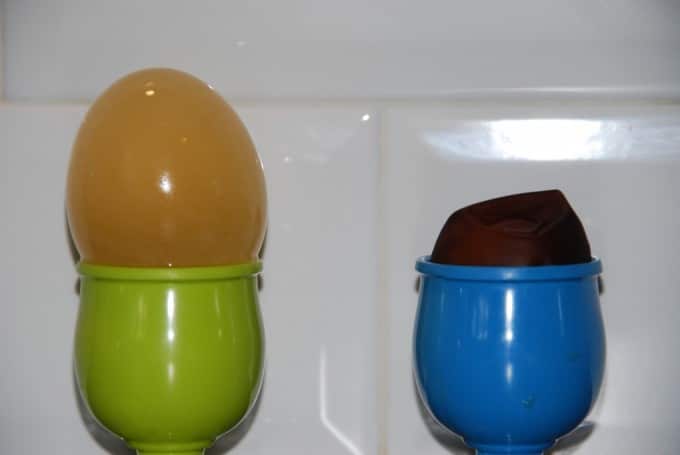
Place the egg in a cup or jar of water and leave for two hours. Water will move into the egg by osmosis as the concentration of water inside the egg is lower than outside. The egg will grow in size.
If the egg is placed in a concentrated sugar solution, water will move out of the egg into the sugar solution as the concentration of water inside the egg is greater than the sugar solution.

More Biology experiments and activities for kids
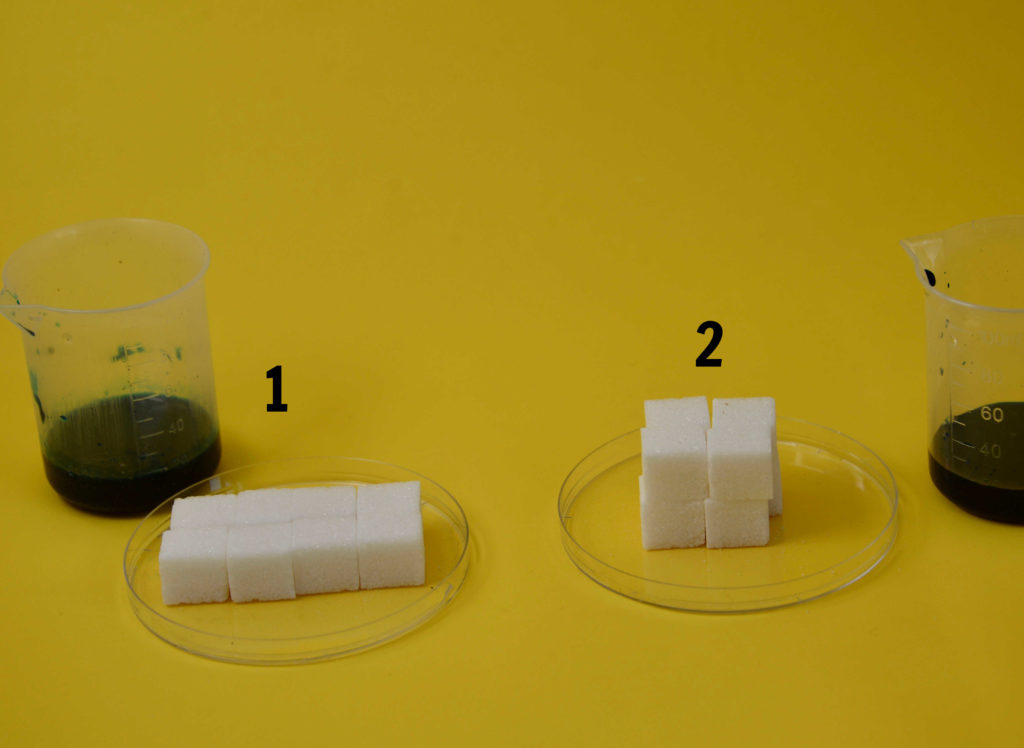
Find out why surface area to volume ratio is such an important concept in biology using sugar cubes.
Learn about Mitosis with paper plate models.
Extract your own DNA at home!
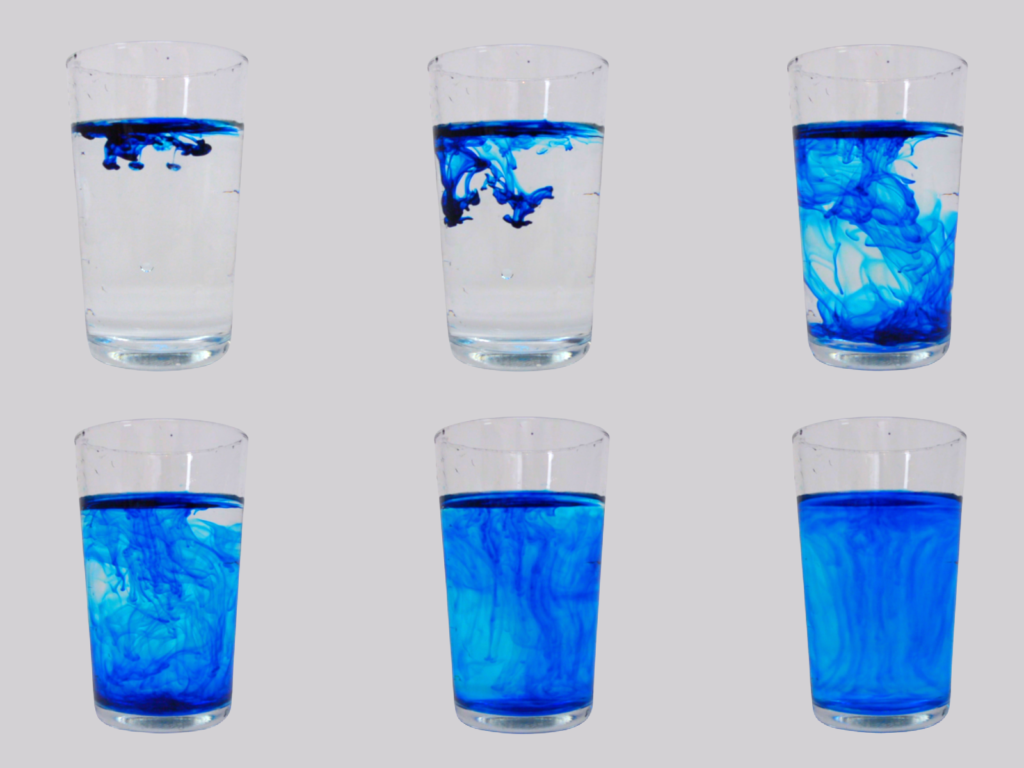
Demonstrate how diffusion works with squash or food colouring and water.

Make plasticine models of viruses to learn about their structure.
Learn about the structure of DNA with this candy model that shows the double helix structure of DNA.
Find out how trees disperse seeds with my selection of seed dispersal activities.
Model the digestive system with a pair of tights! This is an excellent way for children to really visualise how food passes through the human body.

Make a model of a pumping heart to discover why heart valves are so important.
Biology resources on the web
Learn.Genetics has lots of brilliant resources about genes, human health, neuroscience and ecology.
For younger children, check out Maddie Moate on YouTube. The channel covers topics from finding out how cinnamon grows to beekeeping, all explained in a fun and visual way.
Can you recommend any other biology experiments for kids for us to try?

Last Updated on June 30, 2025 by Emma Vanstone



Leave a Reply